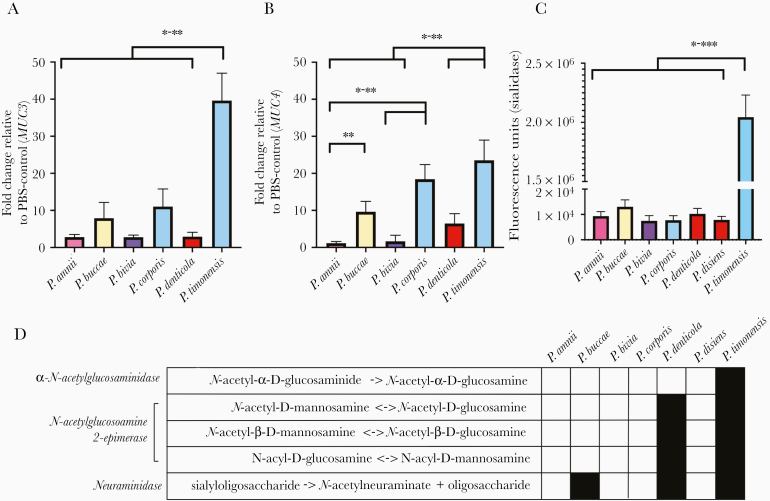
Figure 4.
The molecular interactions between P. timonensis and human 3-dimensional endometrial epithelial cell model rely on mucin metabolism. Relative expression levels of membrane-associated mucins (A) MUC3 and (B) MUC4 in comparison to phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) treated cells. P. timonensis, P. buccae, and P. corporis induced significantly higher levels of MUC3 and MUC4. C, Sialidase activity of the selected Prevotella strains. P. timonensis had more than 1000-times greater sialidase activity in comparison to the representative Prevotella strains. P. bivia VPI6822 was selected to represent Prevotella strains. Data are representative of at least 3 independent experiments. D, Predictions of enzymatic reactions involved in mucin degradation or metabolism based on Prevotella genomes in MetaCyc database. P. denticola and P. timonensis strains are predicted to contain genes that can metabolize mucins. P. timonensis harbors another gene that encodes transformation of mucins. Strain designations: P. amnii CRIS 21A-A, P. buccae D17, P. bivia VPI6822, P. corporis MJR7716, P. denticola DNF00960, and P. timonensis CRIS 5C-B1. Tukey’s multiple comparisons results: *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001.