Figure 3.
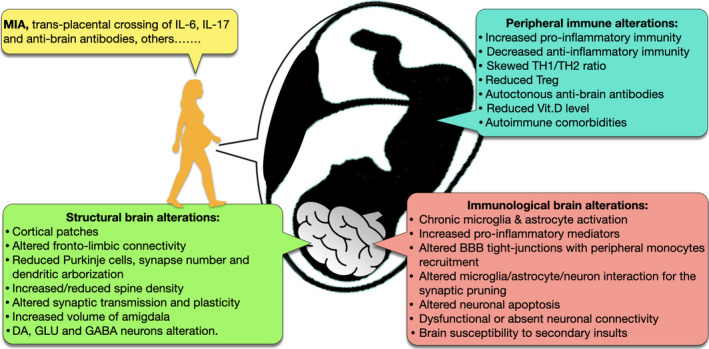
Main structural and immunological brain alterations in autism are linked to an abnormal maternal immune activation (MIA) and, in humans, are also possibly linked to the transdecidual crossing of pro‐inflammatory cytokines and autoantibodies against foetal brain antigens. Peripheral immune alterations of the foetus are mainly of the innate type. IL = interleukin; DA = dopaminergic; GLU = glutamatergic; GABA = γ‐aminobutyric acid; NK/KIR = NK/killer cell immunoglobulin‐like receptor; TH = T helper cells; Treg = T regulatory cells; Vit.D = vitamin D; BBB = blood–brain barrier.
