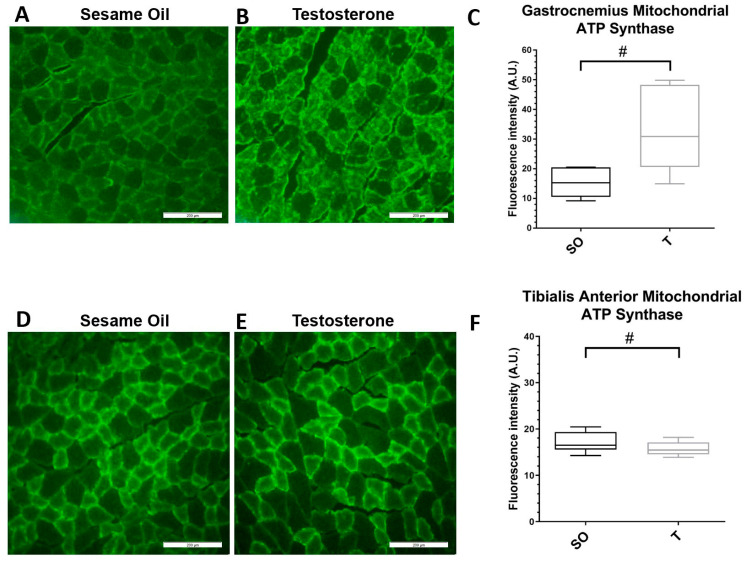
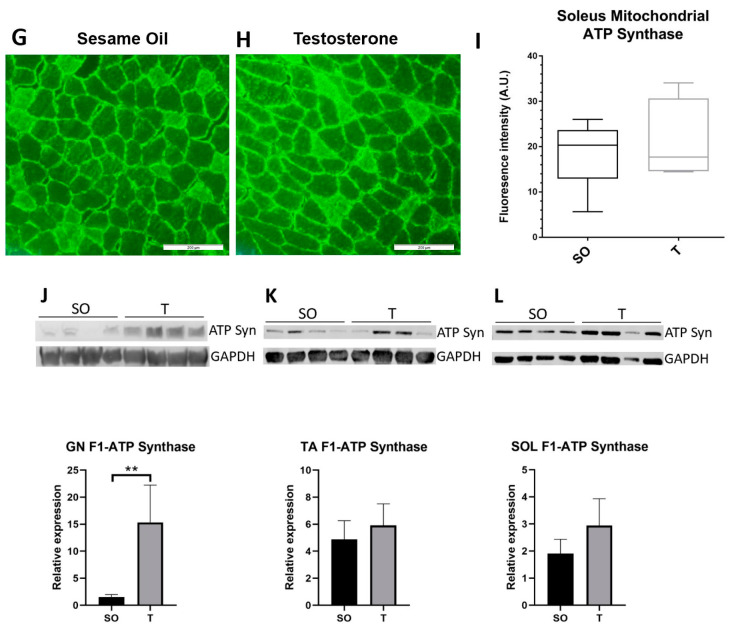
Figure 6.
Expression of the mitochondrial marker ATP synthase is higher in gastrocnemius muscle in PNA rats. Gastrocnemius (A–C), tibialis anterior (D–F), and soleus (G–I) skeletal muscles from 16-week-old female rats exposed to sesame oil (n = 4–5) or testosterone (n = 4–5) were cryosectioned at 20 µm thickness prior to indirect immunolabeling for ATP synthase. Scale bars, 200 µm. For each rat, 3 distinct fields per muscle sample were imaged and the fluorescence intensity quantified (C,F,I). Fluorescence intensity data were analyzed using a Mann–Whitney U test. Fluorescence intensity trended higher in muscles from PNA rats for gastrocnemius (# p = 0.0556), trended slightly lower in TA (# p = 0.0979), but was not significantly different in soleus muscle. Quartiles with the median are shown. (J–L) Protein expression was examined by Western blot and quantified by densitometric analysis. Samples of (J) GN, (K) TA, and (L) SOL muscles from rats exposed to sesame oil (n = 8) or testosterone (n = 8) were separated by SDS-PAGE and transferred to nitrocellulose prior to detection with antibodies to the alpha subunit of ATP synthase or GAPDH (top panels). Values for ATP synthase were normalized to GAPDH and analyzed using an unpaired t test or Mann–Whitney U test, which indicated significantly greater expression of ATP synthase in GN, but not TA or SOL, from PNA rats (bottom panels). Values shown are means with SD. ** p < 0.005.