Figure 1.
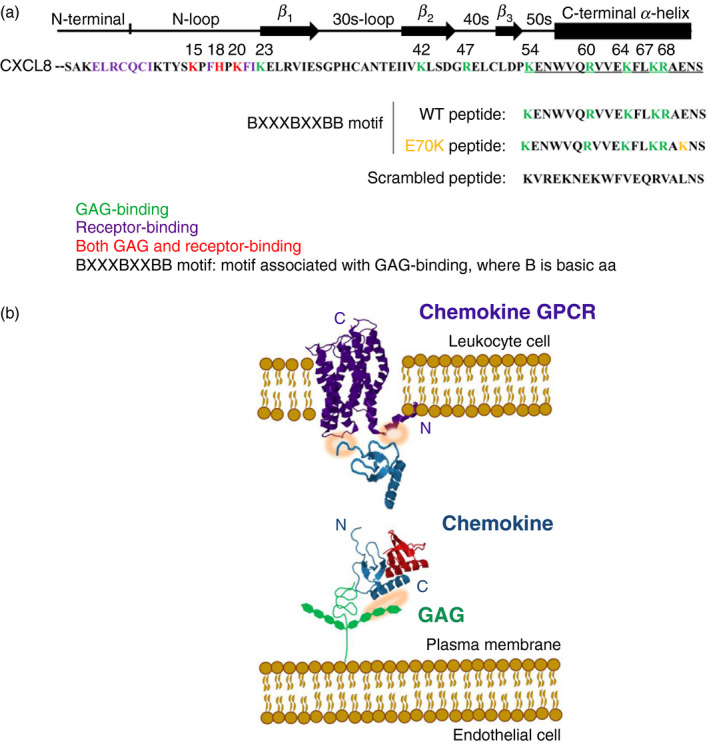
(a) CXCL8 active sequence. (b) Schematic representation of the chemokine binding to the endothelial glycosaminoglycan (GAG) and to the leucocyte chemokine G‐protein coupled receptor (GPCR). (a) Sequence of the most common active CXCL8 form (amino acids 28–99), with 72 amino acids. Green: GAG‐binding residues. Purple: GPCR‐binding residues. Red: residues involved in both GAG‐ and receptor‐binding. Underlined amino acids: C‐terminal α‐helix region selected for chemical synthesis. (b) Schematic representation of chemokine (Protein Data Bank ID 1IL‐8/CXCL8) interaction with endothelial surface through GAG (residues involved highlighted in orange), which enables subsequent high‐affinity chemokine binding to leucocyte CXCR1/2 GPCR receptor (Protein Data Bank ID 2LNL; also highlighted in orange). Chemokine monomer is shown in blue and the dimer is depicted with one molecule in blue and the other in red. Note that illustration shows one potential scenario of chemokine binding.
