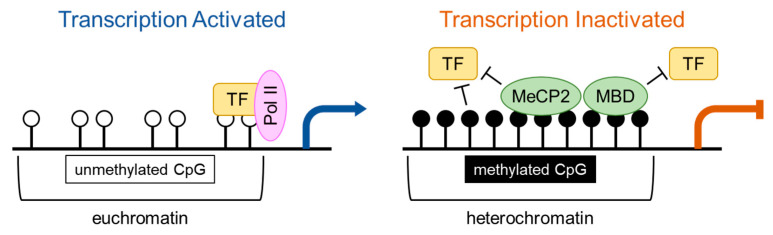
Figure 2.
DNA methylation mediates gene silencing. In euchromatin (loose or open chromatin), cytosine-phospho-guanine dinucleotide (CpG) sites are generally unmethylated in promoter region and accessible to transcription factors (TFs). Methylation of cytosine in CpG sites is associated with heterochromatin (tight or closed chromatin) that typically results in silencing of gene transcription. Methylated CpG prevents the binding of TFs directly or indirectly by interacting with readers of DNA methylation, such as methyl CpG binding protein-2 (MeCP2) and methyl-CpG-binding domain (MBD). Pol II indicates DNA-dependent RNA polymerase II.