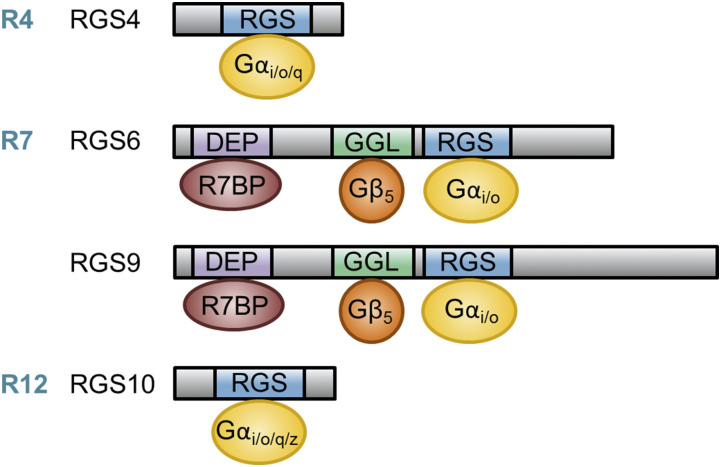
Fig. 2.
Comparison of the protein structure and interaction partners for RGS proteins implicated in PD and proper motor function. RGSs 4, 6, 9, and 10 have been implicated in PD pathogenesis and proper motor function. RGS4 is a member of the R4 RGS subfamily that, through its RGS domain, functions as a GAP for Gαi/o/q. RGSs 6 and 9 are members of the R7 RGS subfamily that, through their RGS domains, function as GAPs for Gαi/o. Members of the R7 subfamily are characterized by two unique domains outside of their RGS domain, the DEP/DHEX domain and the GGL domain. The DEP/DHEX domain allows R7 family members bind to the membrane anchor proteins R7BP or R9AP, whereas the GGL domain promotes interaction with Gβ5, which is required for stabilization of all R7 family members. RGS10 is the smallest RGS protein (∼20 kDa) and is a member of the R12 RGS subfamily, thus functioning as a GAP for Gαi/o/q/z.