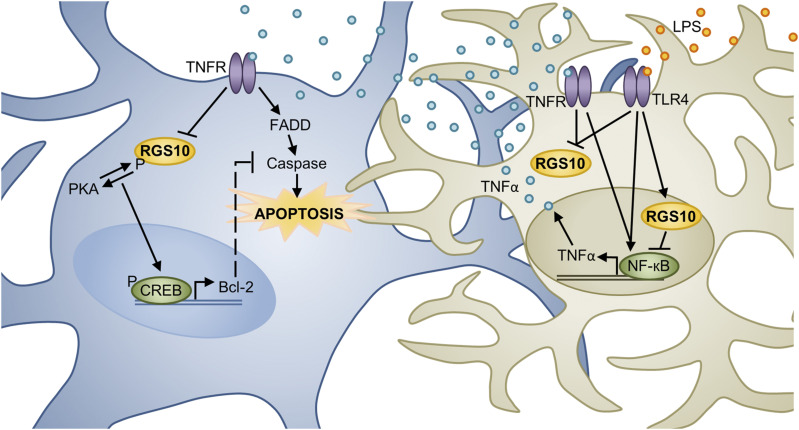
Fig. 6.
Model of RGS10’s role in modulating SNc DA neuron survival. TNFα, an inflammatory factor, can induce neuronal cell death through activation of the TNFR-Fas–associated protein with death domain (FADD)-caspase pathway. Cell culture studies suggest that PKA phosphorylated RGS10 directly promotes MN9D DA cell survival by potentiating PKA-mediated CREB activation and prosurvival gene (Bcl-2) expression. However, RGS10 may also promote cell survival indirectly by inhibiting TNFR/TLR4 (LPS receptor)-NF-кB–mediated inflammatory factor (i.e., TNFα) expression by microglia, the brain’s resident immune cells. Whether acting directly or indirectly to promote DA cell survival, TNFα works to counteract RGS10’s positive effects by reducing its expression. This diagram depicts a microglial cell (tan) in close association with a DA neuron (blue) in the SNc. However, the role of RGS10 SNc DA neurons in vivo has yet to be directly examined. FADD, Fas-associated protein with death domain; LPS, bacterial lipopolysaccharides; TLR4, toll-like receptor 4.