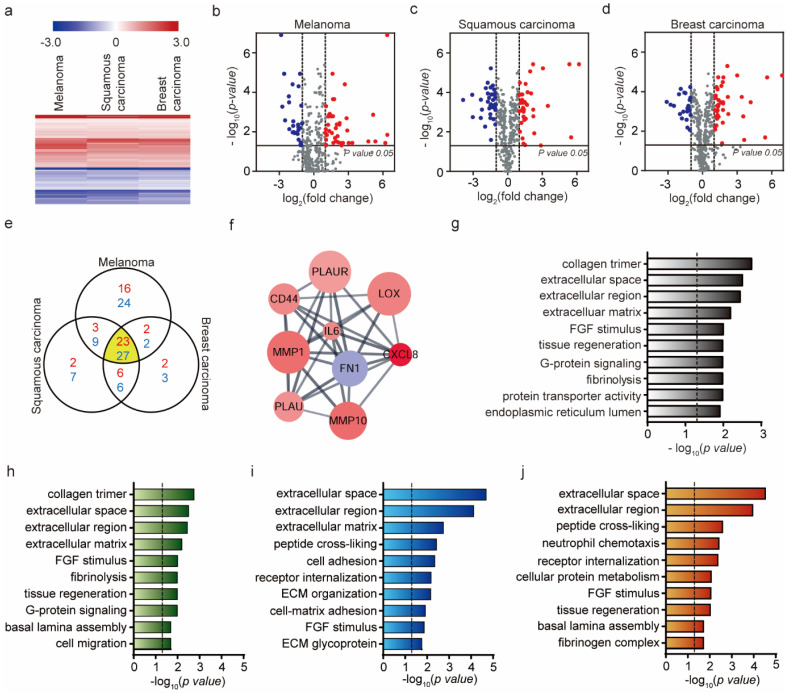
Figure 2.
Identification of differentially expressed genes from eCAFs and their biological functions. (a) Hierarchical clustering of expression profiles of differentially expressed mRNAs among three eCAFs (the eCAFs were produced by the exosomes extracted from B16BL6, A431 and MDA-MB-231 cells) (p-value < 0.05). Red color indicates high relative expression and blue indicates low relative expression. (b–d) Volcano plot showing gene expression differences among the three eCAFs. Red, DE genes with log2 (fold change) > 1; blue, DE genes with log2 (fold change) < −1. (e) Venn diagram showing differentially expressed overlapping gene numbers for three eCAFs. The number of overlapping regions shows the largest number of differentially expressed genes. Red represents log2 (fold change) > 1 and blue represents log2 (fold change) < −1. (f) Top module of the protein–protein interaction (PPI) network for densely connected nodes. Red, DE genes with log2 (fold change) > 1; blue, DE genes with log2 (fold change) < −1. Larger node size is associated with a more significant p-value. (g) Gene ontology (GO) term enrichment analysis of common mRNA expression in three eCAFs (p-value < 0.05, | log2 (fold change) | > 1). (h–j) Gene ontology (GO) term enrichment analysis of expressed mRNA; B16BL6, A431, MDA-MB-231 cells (p-value < 0.05, | log2 (fold change) | > 1). The dashed line signifies p-value of 0.05.