Figure 3.
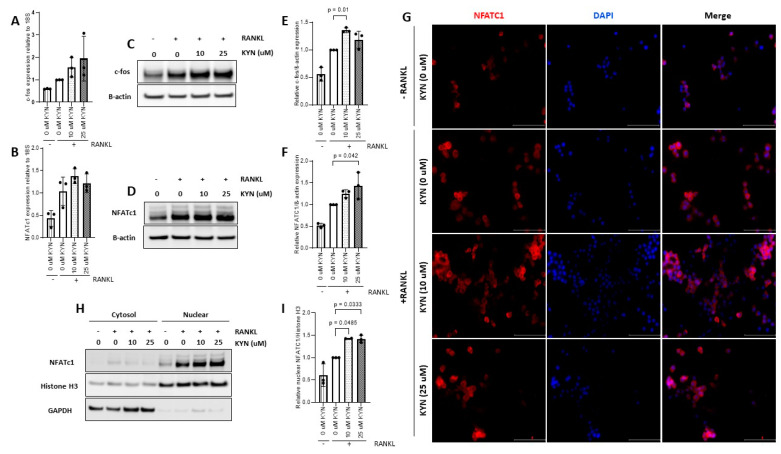
Kynurenine (KYN) treatment upregulates the expression of osteoclast differentiation markers c-fos and NFATc1. mRNA expression level of c-fos (A) or NFATc1 (B) in Raw 264.7 cells treated with KYN (10 or 25 μM) in presence of RANKL for 24 h. Data are presented relative to RANKL-only (0 μM KYN) control. Data are representative of three independent experiments and presented as mean ± SD. One-way ANOVA test was applied. Representative Western blotting of c-fos (C) or NFATc1 (D) proteins in Raw 264.7 cells treated with KYN (10 or 25 μM) in presence of RANKL for 24 h. (E) Densitometric analysis of c-fos protein expression in (C). (F) Densitometric analysis of NFATc1 protein expression in (D). Data are expressed as c-fos/β-actin or NFATc1/β-actin ratio relative to RANKL-only (0 μM KYN) control. Data are representative of three independent experiments and presented as mean ± SD. One-way ANOVA test was applied. (G) Immunocytochemistry analysis of Raw 264.7 cells treated with KYN (10 μM or 25 μM) in presence of RANKL for 24 h using NFATc1 (red) antibody. Nuclei were visualized using DAPI (blue). Images are representative of two independent experiments. Images were taken at 40X objective magnification with scale bar indicated. (H) Representative Western blotting of cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions of NFATc1 in Raw 264.7 cells treated with KYN (10 or 25 μM) in the presence of RANKL for 24 h. Histone H3 was used as nuclear marker and GAPDH was used as cytoplasmic marker. (I) Densitometric analysis of nuclear NFATc1 localization. Data are expressed as NFATc1/Histone H3 ratio relative to RANKL-only (0 μM KYN) control. Data are representative of three independent experiments and presented as mean ± SD. A one-way ANOVA test was applied.