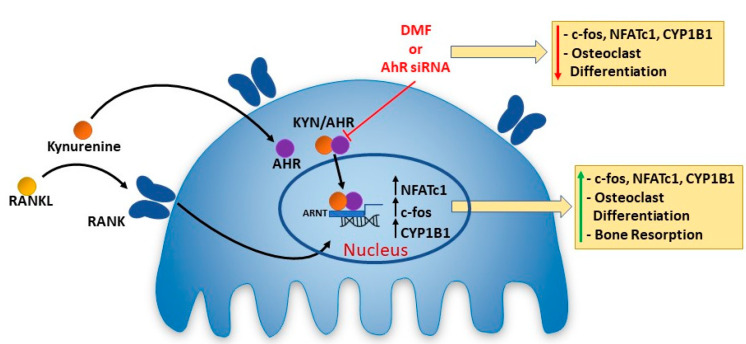
Figure 5.
Kynurenine Induces Osteoclastogenesis Via the AhR Signaling Pathway. In the presence of RANKL, KYN induces Raw 264.7 cells to undergo osteoclastogenesis. This is mediated by KYN binding to AhR which translocates to the nucleus. Based on the literature the ligand bound to AhR forms a transcription factor complex with ARNT [12]. This complex binds to the Xenobiotic responsive elements in the promotor regions of target genes, which here include c-fos, NFATc1 and CYP1B1 [43,45,46,47]. The down-stream consequence is osteoclast differentiation and activation of osteoclast bone resorption. These effects can be blocked by pharmacologic inhibition of AhR with the DMF, or genetic inhibition with AhR siRNA. This suggests that inhibiting KYN levels, blocking KYN binding of AhR, or blocking KYN/AhR signaling may be potential therapeutic approaches to limit the role of osteoclast activity in age-associated bone loss or osteoporosis.