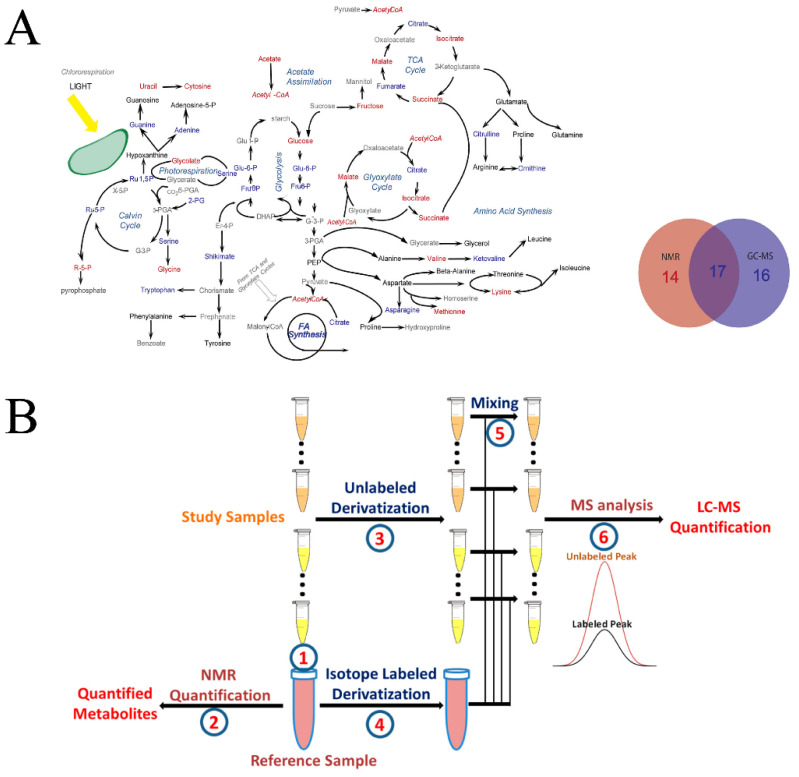
Figure 6.
Metabolite Quantification in Combined Metabolomics. (A) shows the metabolite pathway summery of Chlamydomonas reinhardti metabolome from combined NMR (red) and GC–MS (blue) techniques. Metabolites identified by both methods are colored black, and metabolites that are not identified are colored gray. The embedded Venn diagram identifies total number of metabolites within these metabolomic pathways. Reprinted with permission from Bhinderwala, F.; Wase, N.; DiRusso, C.; Powers, R., Combining Mass Spectrometry and NMR Improves Metabolite Detection and Annotation. Journal of Proteome Research 2018, 17, 4017–4022. Copyright 2018 American Chemical Society. (B) The overall analytical strategy to combine NMR and LC–MS for the absolute quantification of amino acids in serum samples. Step 1: Prepare a reference sample with similar matrix to study samples. Step 2: Divide the reference sample into two portions. The first portion will be examined to determine the metabolite concentrations using qNMR. The other portion will be used in Step 4. Step 3: Derivatize each individual sample under investigation with an unlabeled tag. Step 4: Derivatize the second portion of the reference sample with an isotope-labeled reagent (same reagent used in Step 3). Step 5: After derivatization, mix each individual sample with the reference sample in a 1:1 (v:v) ratio. Step 6: The mixture is then subjected to MS analysis. Given the determined concentrations of metabolites in the reference sample from Step 2, the metabolite concentrations in each study sample can be easily calculated on the basis of the ratio between the labeled and unlabeled MS peaks. Reprinted with permission from Fei, Q.; Wang, D. F.; Jasbi, P.; Zhang, P.; Gowda, G. A. N.; Raftery, D.; Gu, H. W., Combining NMR and MS with Chemical Derivatization for Absolute Quantification with Reduced Matrix Effects. Analytical Chemistry 2019, 91, 4055–4062. Copyright 2019 American Chemical Society.