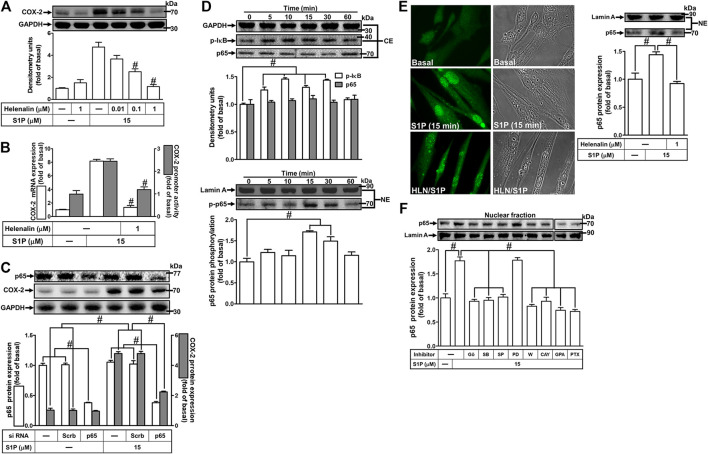
FIGURE 8.
NF-κB is essential for S1P-induced COX-2 expression. (A) Cells were pretreated with helenalin for 1 h and then incubated with 15 μM S1P for 8 h. (B) Cells were transfected without or with COX-2 promoter-luciferase reporter gene, pretreated without or with helenalin (1 μM) for 1 h, and then incubated with 15 μM S1P for 4 h (mRNA) or 1 h (promoter). The levels of COX-2 protein, mRNA expression, and promoter activity were determined by Western blot, real time-PCR, and promoter assay, respectively. (C) Cells were transfected with siRNA of p65 and then exposed to S1P for 8 h. (D) Cells were incubated with S1P (15 μM) for the indicated time intervals. (E) Cells were treated with S1P (15 μM) for 15 min in the absence or presence of helenalin (1 μM). (D,E) The nuclear and cytosol fractions were prepared and analyzed by Western blot. The p65 NF-κB translocation by S1P was also determined by immunofluorescent staining as described in Materials and Methods. (F) To determine which S1PR subtypes, Gi or Gq protein, and MAPKs involved in S1P-stimulated the nuclear localization of p65 NF-κB, cells were incubated with S1P (15 μM) for 15 min in the absence or presence of Gö6976 (Gö, 10 μM), SB202190 (SB, 30 μM), SP600125 (SP, 10 μM), PD98059 (PD, 10 μM), W123 (W, 10 μM), CAY (10 μM), GPA2A (GPA, 10 μM), or PTX (100 ng/ml), and the nuclear fraction was analyzed by Western blot. To fit the construct of data layout, the data were rearranged from the same gel with the exception of non-related inhibitors and disclosed by the insertion of white spaces rearranged from the original capture. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM of three individual experiments (n = 3). # p < 0.05, as compared with the cells treated with S1P alone.