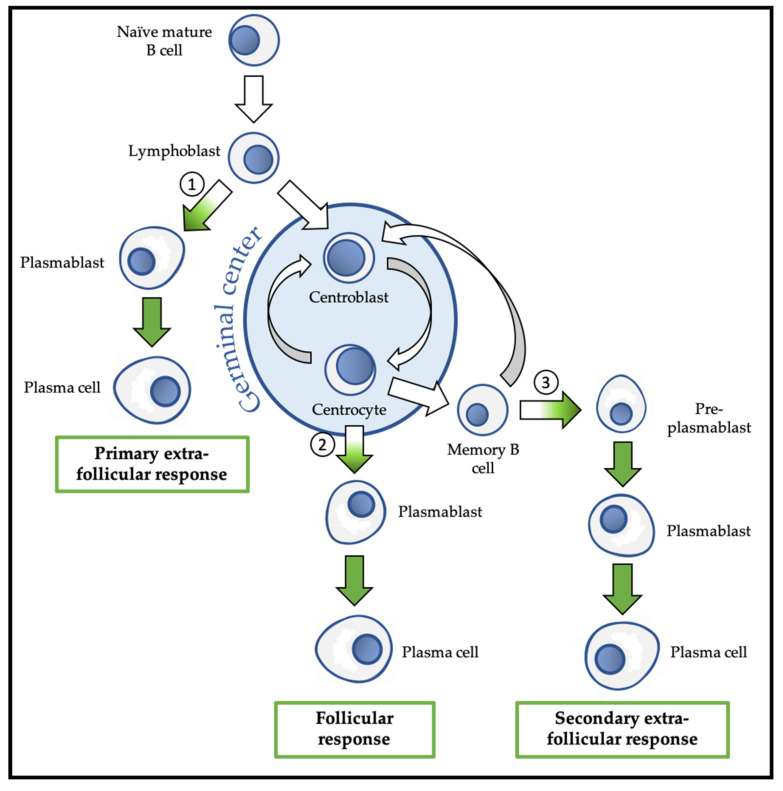
Figure 3.
Overview of physiological differentiation of plasma cells (PC). Upon primary antigen contact, naïve mature B cells are activated and become lymphoblasts that can choose between two pathways: the primary extra-follicular response and the primary follicular response. In the primary extra-follicular response, lymphoblasts immediately differentiate into plasmablasts (PB) then into short-lived PC and produce immunoglobin M (IgM). In the primary follicular response, lymphoblasts enter a lymphoid follicle and form a germinal centre, while differentiating into centroblasts and then centrocytes. During the germinal centre reaction, immunoglobulin class switch recombination (CSR) and somatic hypermutation (SHM) take place. After selection, the centrocytes differentiate either into memory B cells, or into PB and then PC that produce IgG, IgA, or IgE. Upon secondary antigen contact, memory B cells are activated and can choose between a secondary extra-follicular response and a secondary follicular response. The secondary follicular response is similar to the primary follicular response and follows the same steps. In the secondary extra-follicular response, memory B cells immediately differentiate into pre-plasmablasts (pre-PB), PB, and then PC. The numbers indicate the cell fate decision points, where the antibody-secreting cell (ASC) program is switched on. Green arrows indicate cell differentiation steps where the ASC program takes place.