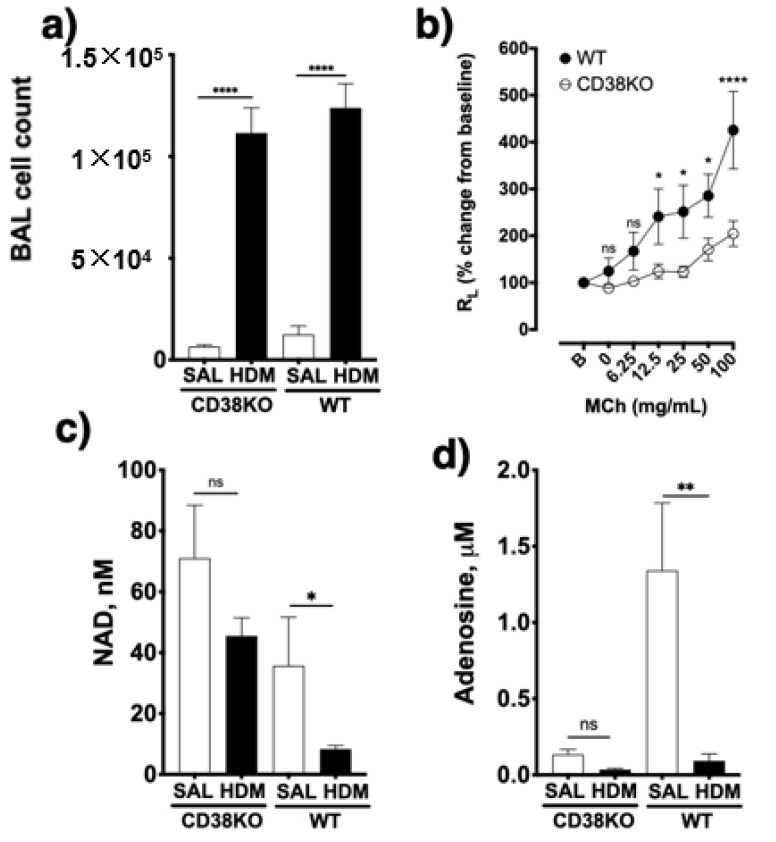
Figure 9.
CD38 activity enhances allergen-induced airway hyperresponsiveness and affect bronchoalveolar levels of NAD+ and adenosine. (a) Wild-type (WT) and CD38KO mice (n = 6–12/group) were intranasally challenged with house-dust mite (HDM) extract for 2 weeks. Allergen challenge significantly increased the inflammatory cell numbers in the bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid compared to saline (SAL)-challenged WT and CD38KO mice. (b) Airway responsiveness to inhaled methacholine was significantly greater following allergen challenge in WT than in CD38KO mice. (c) Allergen challenge significantly decreased NAD+ concentrations in the BAL fluid in WT but not in CD38KO mice. (d) Adenosine concentrations decreased significantly in BAL fluid in WT but not in CD38KO mice. ns = not significant, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, **** p < 0.0001; One-way ANOVA (a), (c), (d) or mixed-effect model (b) with Bonferroni post-hoc.