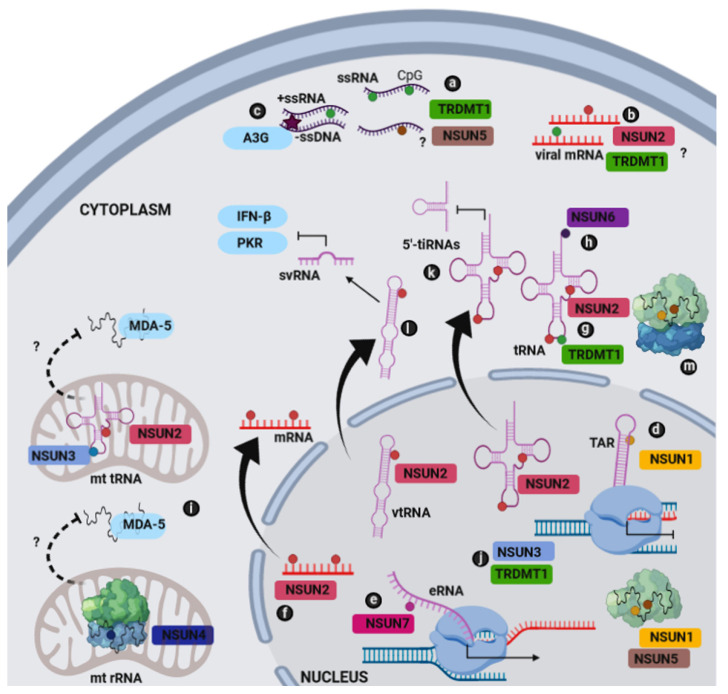
Figure 1.
Overview of human m5C RNA methyltransferases and their RNA targets during viral infections. (a) The methylation of 5′C—phosphate—G3′ (CpG) islands in viral genomic RNA by DNMT2 (TRDMT1) and perhaps NSUN5 may promote viral heterogeneity. (b) The modification of viral transcriptome by NSUN2 and perhaps TRDMT1 may result in increased transcript stability and efficient translation. (c) The cytosine deamination by A3G may lead to dC-to-dU conversions in viral (–)ssDNA that may cause G-to-A hypermutations in progeny viral genomes. (d) Induction of viral latency by NSUN1-mediated m5C methylation of TAR. (e) NSUN7-mediated m5C methylation of eRNA, a transcriptional coactivator of PGC-1α (peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha) and an activator of RNA polymerase II. (f) NSUN2-mediated methylation of viral mRNA promotes its splicing and transport into the cytoplasm (a black arrow). (g,h) NSUN2-, TRDMT1-, and NSUN6-mediated methylation of tRNA molecules protects them against stress-induced degradation and supports efficient translation. (i) Putative protective role of NSUN2-, NSUN3-, and NSUN4-mediated methylation of tRNA and rRNA in the mitochondria. These modification events prevent cytoplasmic translocation of tRNA and rRNA and binding of stress-based degraded form of tRNA and rRNA to a pattern-recognition receptor for RNA (MDA-5) that in turn counteracts the induction of a type I interferon response. (j) NSUN3 and TRDMT1 as putative regulators of RNA polymerase II-mediated gene transcription during cellular stress response. (k) NSUN2-mediated biogenesis of tiRNAs. (l) NSUN2-mediated methylation of vtRNA may promote its conversion to svRNA that, in turn, may inhibit the translation of PKR and IFN-β production. (m) NSUN1- and NSUN5-mediated methylation of rRNA supports ribosome biogenesis and efficient translation. rRNA, ribosomal RNA; tRNA, transfer RNA; mt tRNA, mitochondrial tRNA; eRNA, enhancer RNA; svRNA, specific vtRNA-derived small non-coding RNA; vtRNA, vault RNA; TAR, transactivation response element; tiRNA; tRNA-derived stress-induced RNA, mRNA, messenger RNA; ssRNA, single-stranded RNA; MDA-5, melanoma differentiation-associated protein 5; PKR, RNA-dependent protein kinase; IFN-β, interferon beta; ?-putative action, A3G, apolipoprotein B mRNA editing enzyme catalytic subunit 3G (cytidine deaminase); *- dC-to-dU conversion in viral negative-sense single-stranded DNA (–ssDNA).