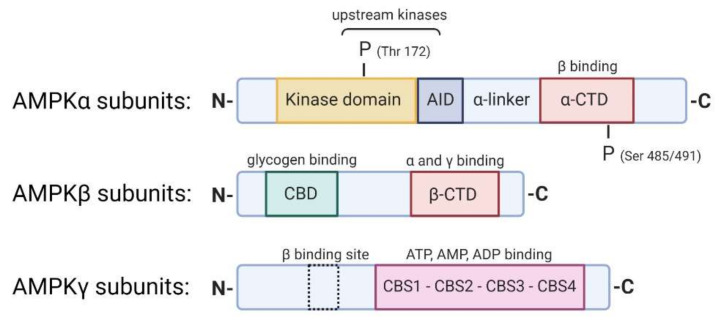
Figure 2.
AMPK α, β, and γ subunits. The crystal structure represents the different domains and specific sites of the α, β, and γ subunits that constitute the AMPK heterotrimeric complex. The AMPKα subunits contain a serine/threonine kinase domain at the N-terminus phosphorylated by upstream kinases on the residue Thr172, directly followed by an autoinhibition domain (AID) that maintains the kinase domain inactive in the absence of AMP and a C-terminus domain (α-CTD) that interacts with the β subunits. Phosphorylation of Ser 485/491 residues on the α-CTD negatively regulates AMPK. The AMPKβ subunits have a glycogen-binding domain (CBD) and an α and γ subunit interaction domain (β-CTD). The AMPKγ subunits present four β-synthase (CBS) domains (CBS1-4) that can bind to ATP, AMP, and ADP. AMP binding initiates the allosteric activation of AMPK and promotes phosphorylation of AMPK by upstream kinases.