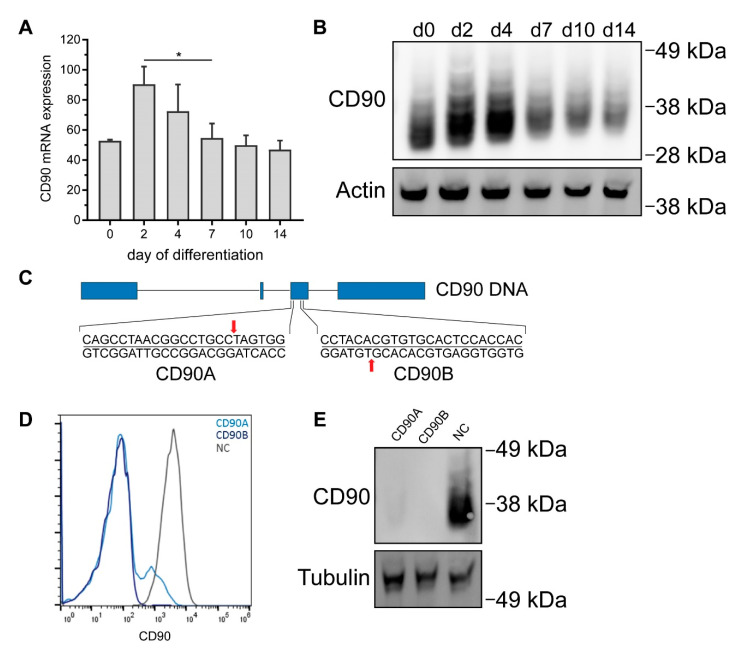
Figure 4.
Generation of CD90-deficient Simpson-Golabi-Behmel syndrome (SGBS) cells using CRISPR/Cas9. Human SGBS cells were subjected to adipogenic differentiation. RNA and protein were isolated on indicated timepoints. (A) CD90 mRNA expression was determined by RT-qPCR. TF2B expression was used to normalize the data. Data are displayed as mean ± SEM of 3 independent experiments. * p < 0.05, one-way ANOVA with Tukey correction (B) CD90 protein expression was determined by Western blot. β-actin was used as a loading control. A representative experiment out of 3 independent experiments is shown. (C) Illustration of CD90 CRISPR/Cas9 knockout strategy. Two different sgRNAs targeting exon 3 of the CD90 gene were used. (D,E) SGBS cells were transfected with plasmids containing a non-targeting sgRNA (NC sgRNA, negative control) or two different sgRNAs targeting CD90 (CD90 A and CD90B). The expression of CD90 in bulk cultures after antibiotic selection was determined by (D) flow cytometry and (E) Western blot. For Western blot, tubulin was used as a loading control. A representative experiment out of 3 independent experiments is shown.