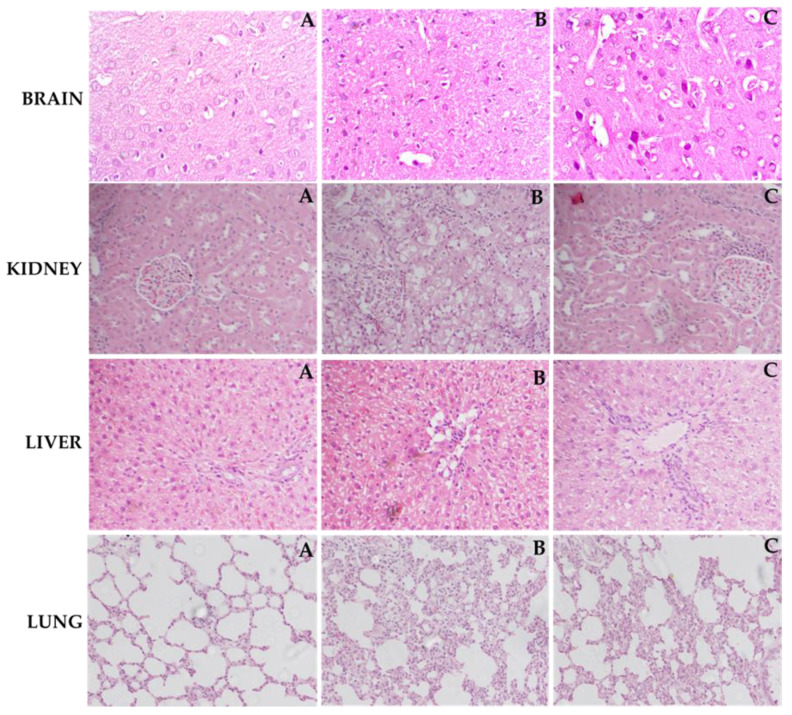
Figure 8.
Light histograms of different rat organs (hematoxylin and eosin stains, magnification 40× and scale bar of 100 µm). Effect of ZIN in LPS intoxicated rats. Brain (A) normal control group: Showing normal histological structure with intact neurons, (B) LPS treated rats: Showing neuronal loss with condensed nuclei, (C) Rats treated with (ZIN 150 mg/kg + LPS: Showing decrease in neuronal loss with presence of intact neurons. Kidney (A) normal control group: Showing normal histological structure of the glomeruli and tubules at the cortex with absence of histopathological alterations, (B) LPS treated rats: Showing marked inflammatory cell aggregation in between the tubules, marked degeneration in the lining epithelium of all the tubules, and blood vessel congestion, (C) Rats treated with (ZIN 150 mg/kg + LPS: Showing absence of histopathological alterations. Liver (A) Normal control group: Showing normal histological structure of the central vein and intact hepatocytes, (B) LPS treated rats: Showing severe loss of hepatic architecture with multiple focal necrosis, ballooning degeneration in the hepatocytes, (C) Rats treated with ZIN 150 mg/kg + LPS: Showing absence of histopathological alterations. Lung (A) Normal control group showing normal morphology, (B) LPS treated rats: Showing moderate to severe hemorrhage, thickening of alveolar septa, emphysema, and infiltration of leukocytes in walls alveoli, (C) Rats treated with ZIN 150 mg/kg + LPS: Showing absence of histopathological changes.