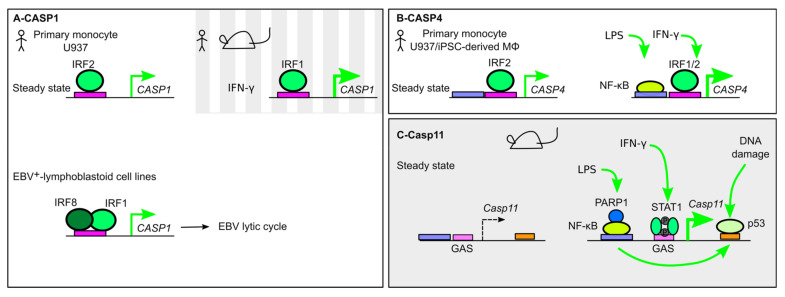
Figure 3.
Transcriptional regulation of inflammatory caspases. (A) In human monocytes, CASP1 expression is regulated at steady state by IRF2, while in the presence of IFN-γ, IRF1 regulates its expression. In Epstein–Barr virus (EBV+) lymphoblastoid cell lines, a ternary IRF1/8/DNA complex controls CASP1 expression and EBV lytic cycle. (B) CASP4 is constitutively expressed in human monocytes in an IRF2-dependent manner. IFN-γ and lipopolysaccharide (LPS) can upregulate CASP4 expression by promoting NF-κB and IRF1 binding to the CASP4 promoter. (C) Casp11 expression is undetectable at steady state but demonstrates a strong upregulation in the presence of LPS or IFN-γ, which promotes the recruitment of NF-κB and STAT1. Poly [ADP-ribose] polymerase 1 (PARP1) acts as a positive cofactor of NF-κB. DNA-damage triggers p53 binding in the Casp11 first intron and induction of its expression. p53 binding is dependent on NF-κB.