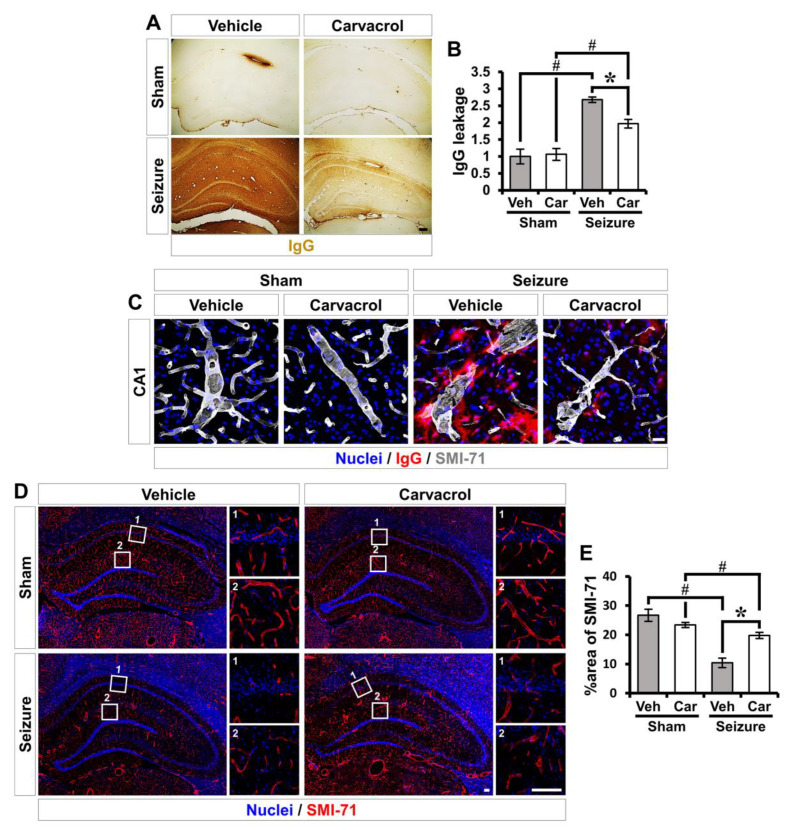
Figure 5.
Carvacrol treatment reduces the blood–brain barrier (BBB) disruption and vessel disappearance following pilocarpine-induced SE. (A) Photomicrographs showing sections of the hippocampus stained for anti-mouse immunoglobulin G (IgG) to detect endogenous IgG. Scale bar, 100 µm. (B) Graph representing IgG leakage from the hippocampus in mice treated with the vehicle or carvacrol at 3 days following pilocarpine-induced SE (mean ± SEM; n = 5 from each sham group, n = 7 from each seizure group). * p < 0.05 vs. the vehicle-treated group; # p < 0.05 vs. the sham-operated group (Kruskal–Wallis test followed by Bonferroni post-hoc test; chi square = 18.493, df = 3, p < 0.001). (C) Double Immunofluorescent images representing the BBB marker SMI-71+ endothelial protein (gray) and endogenous IgG leakage (red) in the hippocampus. Nuclei are counterstained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar = 20 µm. (D) Representative images showing the SMI-71+ endothelial protein (red) in the hippocampus. Nuclei are counterstained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar, 100 µm. (E) Quantification of the percent area of the SMI-71+ endothelial protein in the hippocampus (mean ± SEM; n = 3–4 from each sham group, n = 5–7 from each seizure group). * p < 0.05 vs. the vehicle-treated group; # p < 0.05 vs. the sham-operated group (Kruskal–Wallis test followed by a Bonferroni post-hoc test: chi square = 19.080, df = 3, p < 0.001).