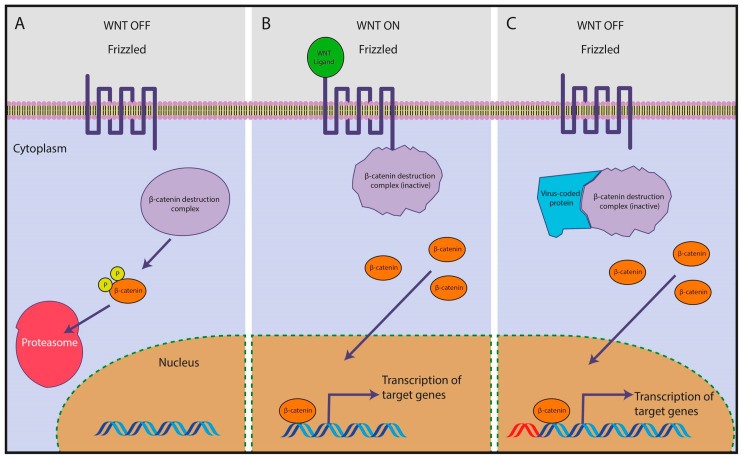
Figure 1.
Virus-mediated modulation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. (A) When Wnt signalization is off, β-catenin is phosphorylated via the β-catenin destruction complex and subsequently degraded by the proteasome. (B) When a Wnt ligand binds a Wnt receptor (Frizzled), the β-catenin destruction complex is inactive, and β-catenin accumulates and enters the nucleus, where it modulates the transcription of target genes. (C) When infecting a cell, a virus may interact with some of the Wnt pathway components (e.g., the β-catenin destruction complex), leading to the accumulation of β-catenin and persistent transcription of its target genes, even in the absence of a Wnt ligand.