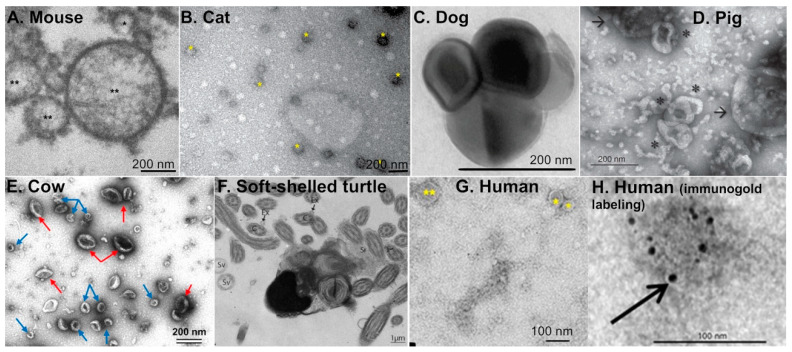
Figure 1.
Transmission electron microscopy images of extracellular vesicles present in the oviductal fluid from different species, including rodents, domestic animals, farm animals, reptiles, and humans. (A) Mouse: exosome (*) and microvesicles (**). Reprint with permission from [23]. (B) Cat: extracellular vesicles (*). Reprint with permission from [28]. (C) Dog: oEVs. Reprint with permission from [25]. (D) Pig: exosomes (*) and microvesicles (arrows). Reprint with permission from [26]. (E) Cow: exosomes (blue arrows) and microvesicles (red arrows) isolated from in vivo oviduct. Reprint with permission from [24]. (F) Soft-shelled turtle: extracellular vesicles (arrows) in the lumen of the oviduct from the isthmus region. Reprint with permission from [27]. C; cilia, Ex; exosome, Sr; oviduct secretions, Sv; secretory vesicles. (G,H) Human: exosomes (*) and microvesicles (**) with or without immunogold labeling. Reprint with permission from [19].