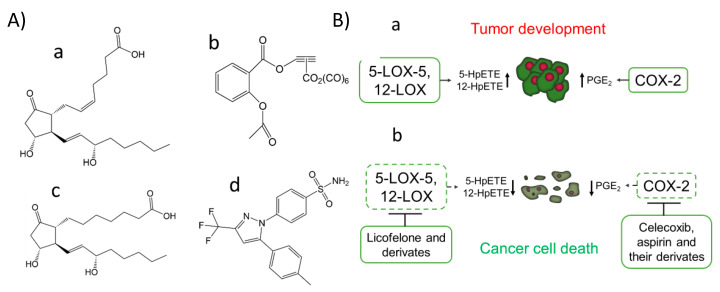
Figure 1.
COX-2 inhibitors, PGE1, and PGE2 chemical structure (A). The prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) (pro-cancer) (a), the aspirin derivate named [2-acetoxy-(2-propynyl)benzoate]hexacarbonyldicobalt (Co-ASS) (b), the prostaglandin E1 (PGE1) (anticancer) (c) and the COX-2 selective inhibitor named celecoxib, (p-(5-p-Tolyl-3-(trifluoromethyl) pyrazol-1-yl)benzenesulfonamide) (d). Expression of COX-2, 5-LOX, and 12-LOX in cancer and the effect of inhibitors against these targets (B). Activation of 5-LOX-5, 12-LOX, and COX-2 has been reported in the development and progress of tumors from different tissues associated with the production of specific lipid peroxides and metabolites, such as PGE2 (a). Some inhibitors of these LOX isoforms and COX-2 have emerged as potential therapeutical agents for cancer treatment, modulating the production of previously commented metabolites and by induction of cancer cell death (b).