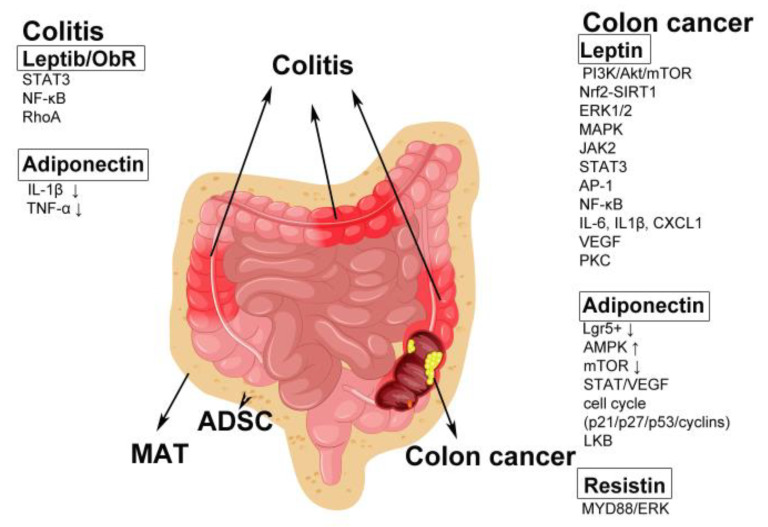
Figure 2.
The adipokine-associated signaling pathways in colitis and colon cancer. The altered adipokine and associated pathways are shown on the left for colitis and on the right for colon cancer. Up arrows: upregulation of the signaling pathways under the stimulation of associated adipokines; down arrows: downregulation of the signaling pathways under the stimulation of associated adipokines. MAT: mesenteric adipose tissue; ADSC: adipose tissue-derived stem cells; ObR: leptin receptor; STAT3: signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; NF-êB: nuclear factor ê-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; RhoA: Ras homolog gene family, member A; IL-1â: interleukin 1â; TNF-á: tumor necrosis factor-á; PI3K: phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; mTOR: mammalian target of rapamycin; Nrf2: nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; SIRT1:silent information regulator 2 homologue 1; ERK1/2: extracellular signal-related kinase 1/2; MAPK: mitogen-activated protein kinase; JAK2: Janus kinase 2; AP-1: activator protein 1; IL-6: interleukin 6; CXCL1: chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 1; VEGF: vascular endothelial growth factor; PKC: protein kinase C;Lgr5+: leucine-rich repeat-containing G-protein coupled receptor 5+; AMPK: MP-activated protein kinase; LKB: liver kinase B1; MYD88: myeloid differentiation primary response 88.