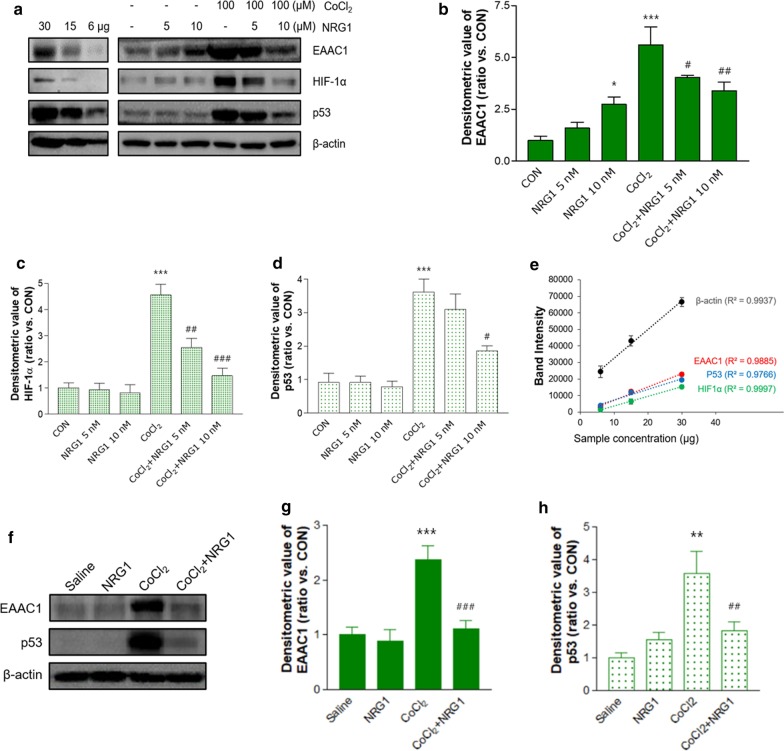
Fig. 2.
The effects of NRG1 on the CoCl2-induced protein levels of EAAC1. a Representative immunoblots of EAAC1, HIF-1α, and p53 in SH-SY5Y cells in the presence or absence of 5 nM or 10 nM NRG1 following treatment with 100 µM CoCl2 for 36 h are shown. Semiquantitative Western blot analysis of EAAC1 (upper panel), HIF-1α (middle panel), and p53 (lower panel) in SH-SY5Y cells. Cell lysates were loaded with a series of 50% and 20% dilutions from the cell extract. b Quantitative analysis of the data in a. Treatment with 100 µM CoCl2 significantly increased the expression of EAAC1. CoCl2-induced EAAC1 overexpression was attenuated by 5 nM or 10 nM NRG1 treatment. The densitometry values are shown as ratios relative to the values of the control group (n = 8; *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001 versus the control group; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01 versus the CoCl2 alone group). c Quantitative analysis of the data in a. CoCl2-induced HIF-1α accumulation was attenuated by 5 nM or 10 nM NRG1 treatment (n = 6; ***P < 0.001 versus the control group; ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001 versus the CoCl2 alone group). d Quantitative analysis of the data in a. CoCl2-induced p53 stability was attenuated by 10 nM NRG1 treatment (n = 6; ***P < 0.001 versus the control group; #P < 0.05 versus the CoCl2 alone group). e Standard curve of semiquantitative Western blot data in a f Unilateral microinjection of CoCl2 into the VH increased the expression of EAAC1 and p53. NRG1 IP injection attenuates the overexpression of EAAC1 and p53. g Quantification of EAAC1 immunoreactivity in f (n = 8; ***P < 0.001 versus the control group; ###P < 0.001 versus the CoCl2 alone group). h Quantification of p53 immunoreactivity in f (n = 8; **P < 0.01 versus the control group; ##P < 0.01 versus the CoCl2 alone group)