Figure 2.
Evaluation of hERG Channel Function in Differentiation Day 21 + 7 KCNH2WT/WT, KCNH2PR/WT, and KCNH2TL/WT hiPSC-CMs
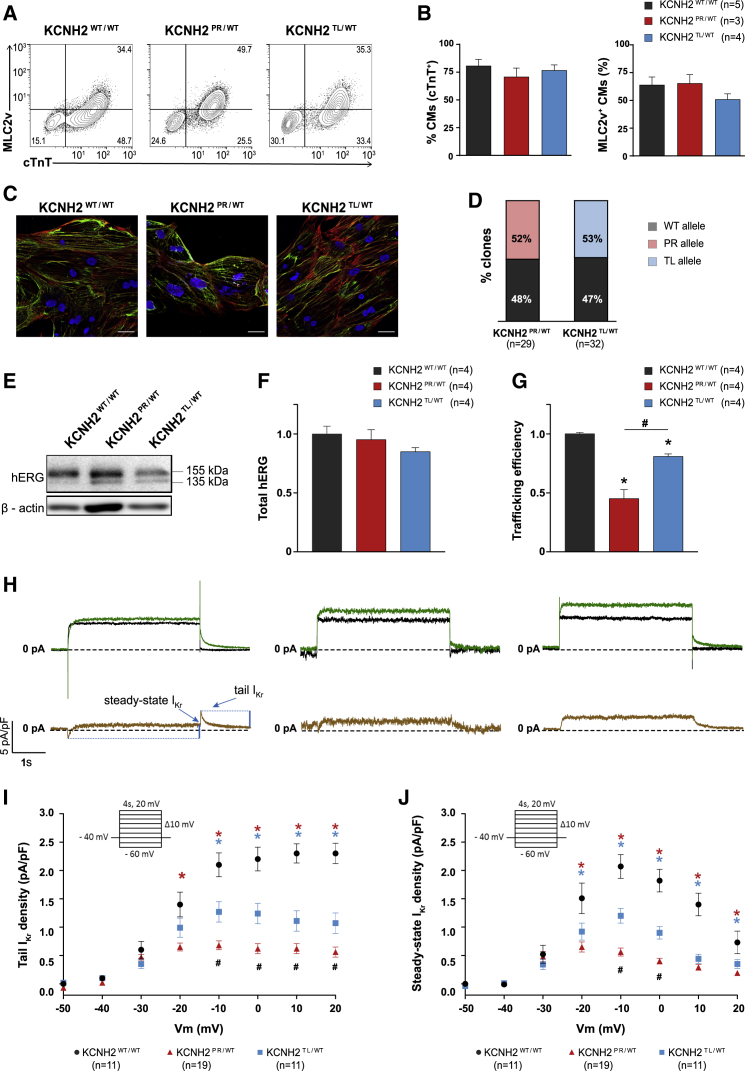
(A) Representative flow cytometry plots of hiPSC-CMs for expression of cTnT and MLC2v in the indicated lines. Values inside the plots are the percentage of cells within the gated region.
(B) Overall cardiac differentiation efficiency of the three hiPSC lines, showing the average percentage of hiPSC-CMs (cTnT+) (left graph), and the proportion of ventricular-like (MLC2v+) cardiomyocytes within the hiPSC-CM population (right graph). Values (n) refer to the number of independent differentiations analyzed.
(C) Immunofluorescence images of the cardiac sarcomeric proteins α-actinin (red) and myosin heavy chain isoforms α and β (green) in the indicated lines. Nuclei (blue) were stained with DAPI. Scale bars, 25 μm.
(D) Percentage of KCNH2 mRNA in the KCNH2PR/WT and KCNH2TL/WT hiPSC-CMs transcribed from the wild-type (WT) or mutated (PR, TL) alleles. Values (n) refer to the number of independent clones sequenced.
(E) Western blot analysis of hERG in the indicated lines. Bands corresponding to core and fully glycosylated hERG (135 and 155 kDa, respectively) are marked. β-Actin was used as a loading control.
(F and G) Densitometric quantification of western blots in (E) and Figure S2C for total hERG protein (155 +135 kDa; relative to KCNH2WT/WT) (F), and the ratio of fully glycosylated over total hERG protein (trafficking efficiency) (G). Data normalized to β-actin. ∗statistical significance to KCNH2WT/WT (p < 0.05); #statistical significance between KCNH2PR/WT and KCNH2TL/WT (p < 0.001); one-way ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparisons test. Values (n) refer to the number of independent differentiations analyzed.
(H) Top panels show representative current traces evoked by a 4-s voltage step from −40 to 0 mV before (green lines) and after (black lines) application of 5 μM E-4031. Bottom panels present the E-4031-sensitive current (brown lines). Arrows indicate the sections of the traces analyzed to determine the tail and steady-state IKr current densities.
(I and J) Average current-voltage relationships for tail (I) and steady-state (J) IKr current densities in the indicated hiPSC-CMs. All CMs activated upon depolarization reached a maximum steady-state current at −10 and 0 mV, which decreased at more positive potentials due to the onset of inactivation. Inset: voltage protocol; ∗statistical significance to KCNH2WT/WT (tail IKr, p < 0.0001; steady-state IKr, p < 0.01); #statistical significance between KCNH2PR/WT and KCNH2TL/WT (tail IKr: −10 mV, 0 mV, p < 0.001; 10 mV, 20 mV, p < 0.01; steady-state IKr: −10 mV, p < 0.0001, 0 mV, p < 0.01); two-way ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparisons test. Values (n) refer to the number of individual hiPSC-CMs analyzed.
Error bars represent SEM.
See also Figure S2.