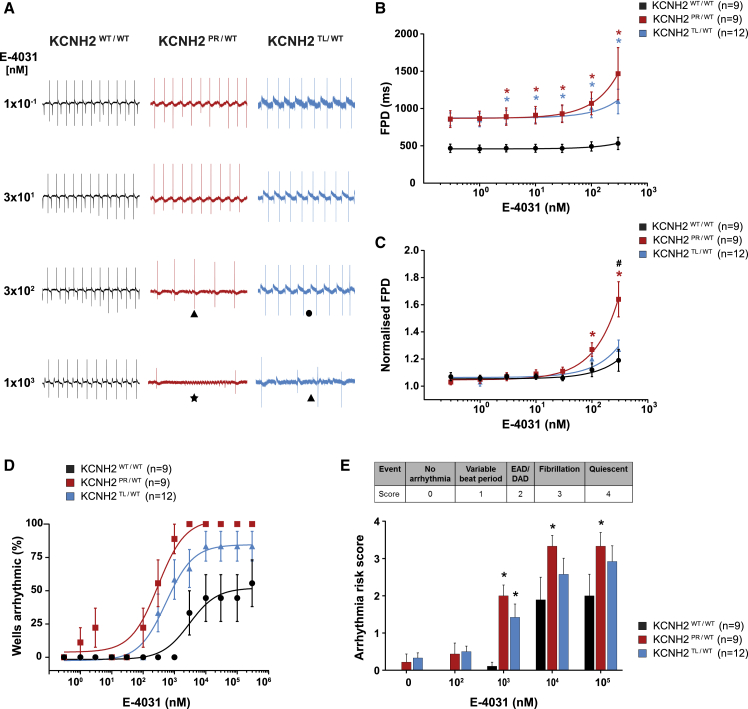
Figure 4.
Effect of IKr Blockade on FPD and Arrhythmogenesis in KCNH2WT/WT, KCNH2PR/WT, and KCNH2TL/WT hiPSC-CMs
(A) Representative MEA traces highlighting the differences between the indicated lines in the development of arrhythmic events during a recording as E-4031 is cumulatively added. Symbols indicate examples of the different types of arrhythmias detected: (•) variable beat period; (▴) abnormal repolarizations; (★) fibrillation.
(B and C) FPD (B) and FPD normalized to baseline (C) of the indicated lines upon accumulative addition of E-4031. ∗Statistical significance to KCNH2WT/WT (FPD: 3–300 nM, p < 0.05; normalized FPD: 100 nM, p < 0.05; 300 nM, p < 0.0001); #statistical significance between KCNH2PR/WT and KCNH2TL/WT (p < 0.0001); two-way ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparisons test.
(D) Scatterplot illustrating relationship between occurrence of arrhythmic events and concentration of E-4031 for the indicated lines. Curve fitting with nonlinear regression.
(E) Arrhythmia risk scoring system and bar graph summarizing the arrhythmia risk for each of the cell lines at different concentrations of E-4031. EAD/DAD, abnormal repolarization; ∗statistical significance to KCNH2WT/WT (p < 0.05; two-way ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparisons test). Values in figure (n) refer to the number of independent wells analyzed from at least three differentiations for each cell line.
Error bars represent SEM.
See also Figure S4.