Fig. 6.
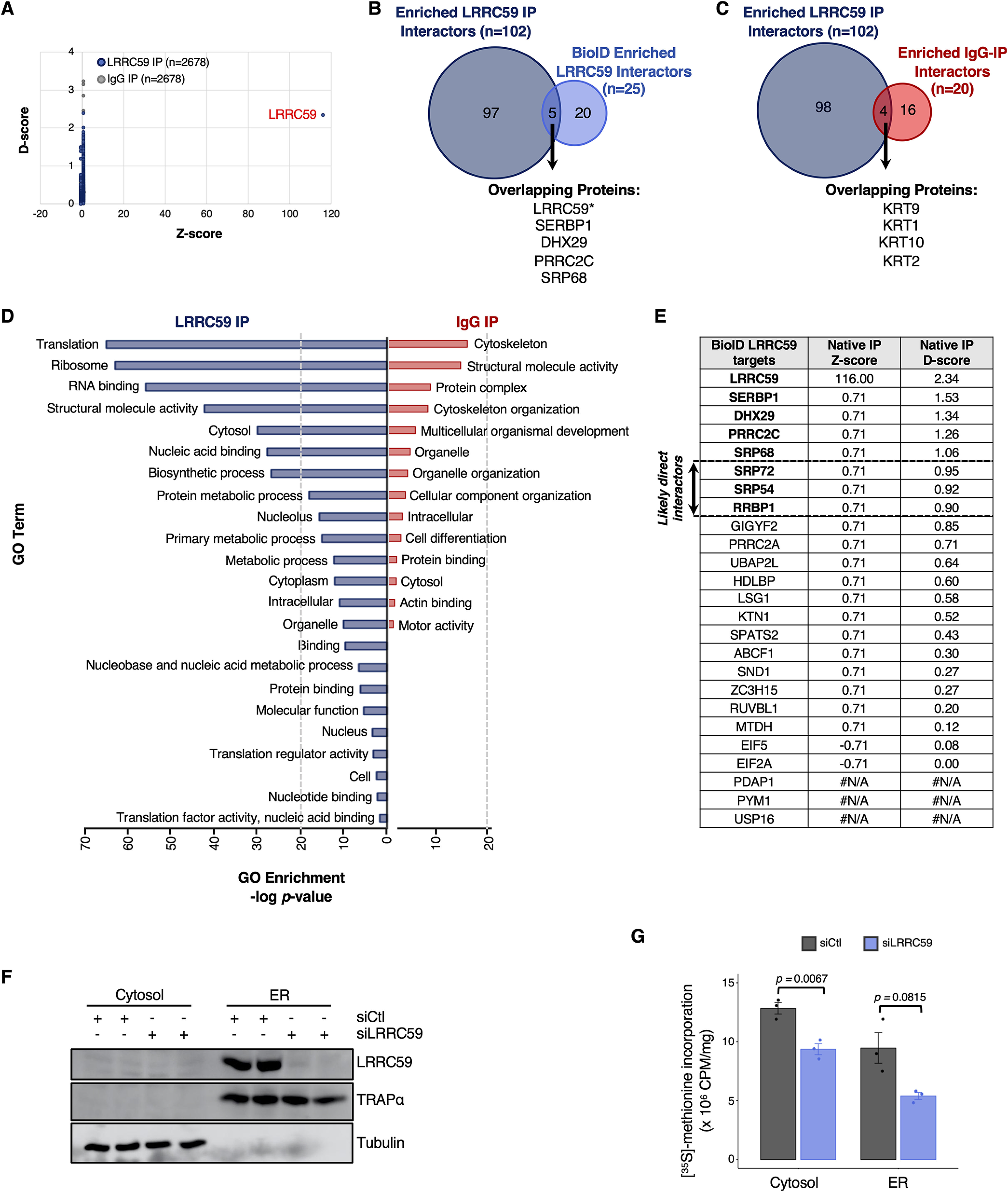
LRRC59 co-IP screen for direct interactions with SRP pathway, translation machinery, and RNA-binding proteins. A, Comparison of D- and Z-scores, as determined by CompPASS analysis, for all proteins identified to interact with LRRC59 (blue) and IgG (control; gray) via immunoprecipitation (IP). Each dot is one of the 2,678 proteins identified by mass spectrometry. B, Number and overlap of enriched, high-confidence interactors of LRRC59, as determined by co-IP (dark blue) or isobaric tagging (BioID; light blue) approaches. C, Number and overlap of high-confidence interactors (D-score ≥ 1) of LRRC59 (dark blue) or IgG (red), as determined by co-IP. D, Enriched Gene Ontology (GO) terms associated with high-confidence LRRC59 interactors (dark blue, left) or IgG interactors (red, right). E, Comparison of D- and Z-scores for each of the 25 LRRC59-interacting proteins, as determined by the BioID approach. F, Western blot analysis depicting LRRC59 expression in cells transfected with either control (scrambled) siRNA or LRRC59-targeted siRNA. Tubulin and TRAPα serve as controls for protein loading and subcellular fractionation, respectively. G, Bar plot showing normalized levels of [35S]-methionine incorporation in the cytosol or ER compartments of non-targeting siRNA (siCtl, negative control) or LRRC59-targeted siRNA transfected cells.
