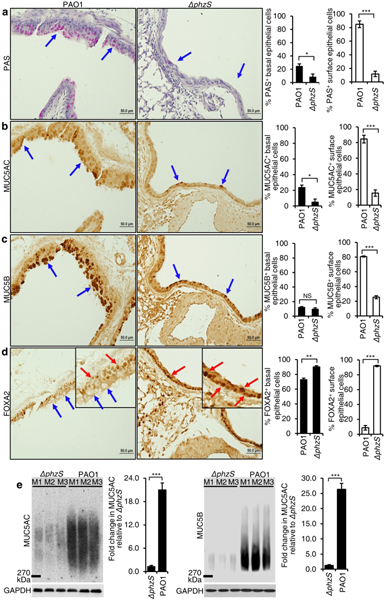
Fig. 2.
Pseudomonas aeruginosa (PA) infection depletes the expression of FOXA2 in a pyocyanin-dependent manner. Six-week old C57BL6 mice (n = 8) were intranasally-infected in chronic bronchitis model with the wild-type PA strain PAO1 or the pyocyanin-deficient mutant ΔphzS, (1 × 106 CFU, Day 1, 3, 5, 7, 1-week duration). Lung sections were stained with Periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) (a, blue arrows), or by immunohistochemistry (IHC) by using antibodies against MUC5AC (b, blue arrows), MUC5B (c, blue arrows), and FOXA2 (d, blue arrows) respectively. Red arrows in d show FOXA2 expression in basal epithelial cells of PAO1-infected airways, and in both basal and surface epithelial cells of Δphz-Sinfected airways. IHC staining was visualized with the M.O.M Immunodetection Kits (FOXA2) and the VECTASTAIN ABC Kits (MUC5AC and MUC5B). a-d, % of basal and surface epithelial cells staining positive for PAS, MUC5AC, MUC5B and FOXA2 were compared by the Student’s t-test. e The expression of secreted MUC5AC and MUC5B in the mouse lungs infected by PAO1 versus ΔphzS. BALF of each mouse was individually analyzed by densitometry, and the mean value of the ΔphzS was then used as the baseline to measure mucins levels induced by the wild-type strain PAO1. All data from a-e are presented as mean ± s.e.m.; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. NS: Not significant.