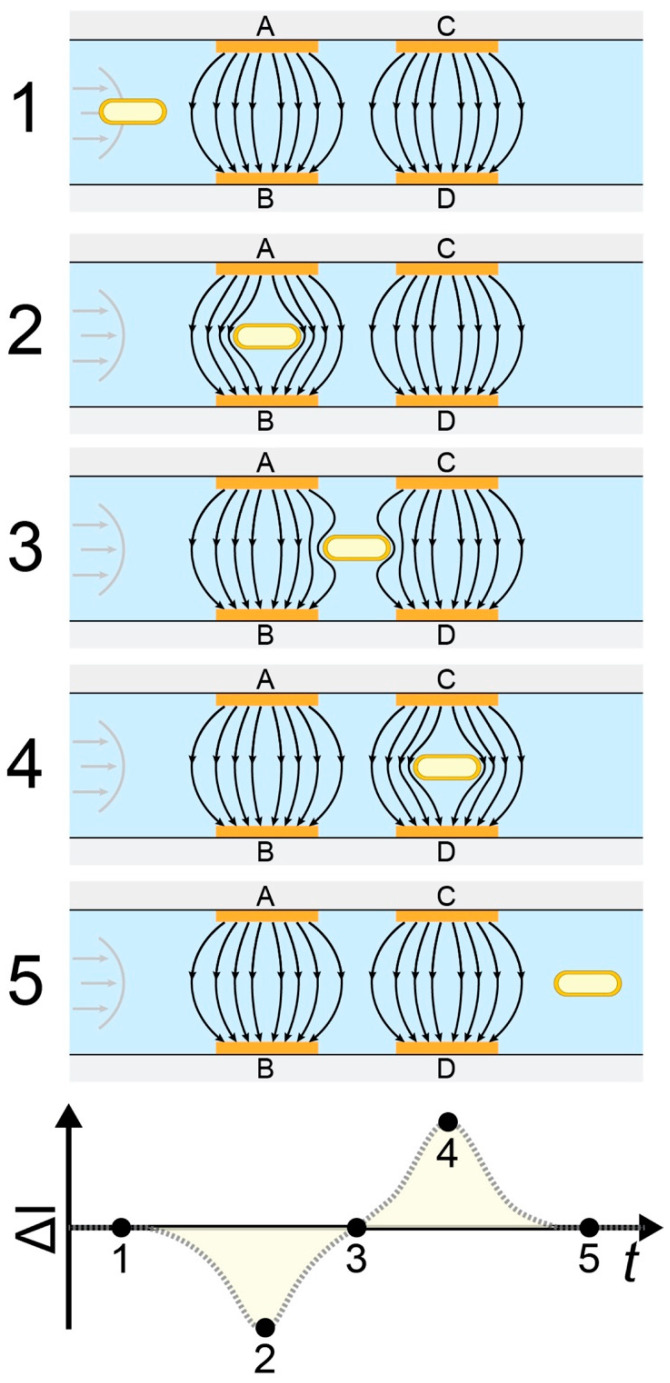
Figure 1.
Detection principle. Schematic of 5 positions of a transitioning bacteria (1, 2, 3, 4, and 5) and the corresponding differential current (ΔI = IAB − ICD). When a bacterium enters the detection area (position 1), the current between the two electrode sets is identical (IAB = ICD), resulting in a differential current of zero. When the bacterium moves between electrodes A and B (position 2), the electric field is perturbed resulting in a non-zero differential current. When the bacterium is exactly between the electrode sets (position 3) the differential current is again zero. As the bacterium transitions between electrodes C and D and further out of the detection area, the electric field is again perturbed giving rise to a differential current (position 4). At position 5, the differential current is again zero as the bacterium exits the detection area.