Figure 2.
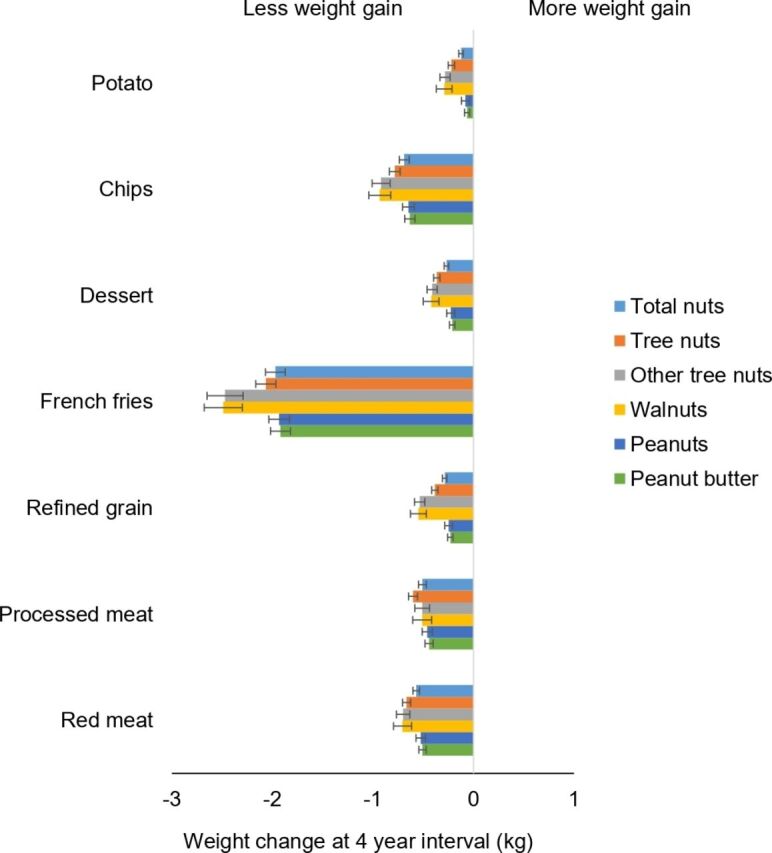
Association of weight change (kg) every 4 years and substitution of nuts, individual types of nuts, per 0.5 servings/day with equal serving of other food items among NHS, NHS II and HPFS. Weight changes are presented as solid bars; T bars represent 95% CI. Multivariate model was adjusted for age, menopausal status (pre- or postmenopausal) and hormone therapy use (never, past, or current) in women; baseline BMI of every 4 years; hours of sleeping at baseline; changes in lifestyle factors: smoking status (never, former, current: 1 to 14, 15 to 24, or ≥25 cigarettes/day), physical activity (MET hours/week), hours of sitting (hours/week); changes in dietary factors: fruits, vegetables, alcohol, snacks, dessert, French fries, red or processed meat, whole grain, refined grain products, and sugar sweetened beverages. The p values are <0.001 for all nuts with the exception of when substituting whole grain with peanut butter in HPFS, whole grain, potato with peanuts, and potato with total nuts in NHS. Data on walnuts and other tree nuts were first available in 1998 for NHS, 1998 for HPFS and 1999 for NHS II. Tree nut consumption was the sum of other tree nuts and walnut (if available). Total nut consumption was the sum of peanut, tree nut and walnut (if available). BMI, body mass index; HPFS, Health Professionals Follow-up Study; MET, metabolic equivalent; NHS, Nurses' Health Study.
