FIGURE 4.
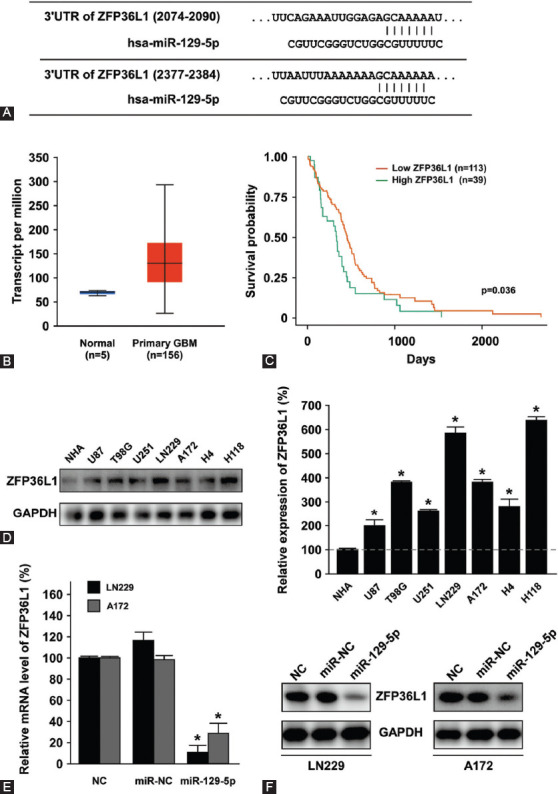
Relationship between miR-129-5p and its downstream target gene ZFP36L1. (A) Prediction of miR-129-5p binding sites in the 3’-UTRs of ZFP36L1 gene by TargetScan analysis. (B and C) Expression of ZFP36L1 and survival analysis in GBM patients using the UALCAN dataset. ZFP36L1 expression was upregulated in GBM tissues (n = 156) compared with normal brain tissues (n = 5). Higher ZFP36L1 expression was associated with poor survival. (D) ZFP36L1 expression was significantly upregulated in GBM cell lines LN229, A172, U87, T98G, U251, H4, and H118 compared with NHA. Differences were found to be statistically significant at *p < 0.05. (E and F) MiR-129-5p negatively regulated the expression of ZFP36L1 in LN229 and A172 cells. Overexpression of miR-129-5p in LN229 and A172 cells significantly suppressed the mRNA level (E) and protein level (F) of ZFP36L1. GAPDH was used as an internal control. Differences between miR-129-5p and miR-NC were found to be statistically significant at *p < 0.05. UTR: Untranslated region; ZFP36L1: ZFP36 ring finger protein-like 1; GBM: Glioblastoma multiforme; NHAs: Normal human astrocytes; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
