Figure S7.
Breakdown of Geography and Genetics among Xiongnu and Comparison of Mongol Period and Present-Day Populations, Related to Figure 3 and STAR Methods
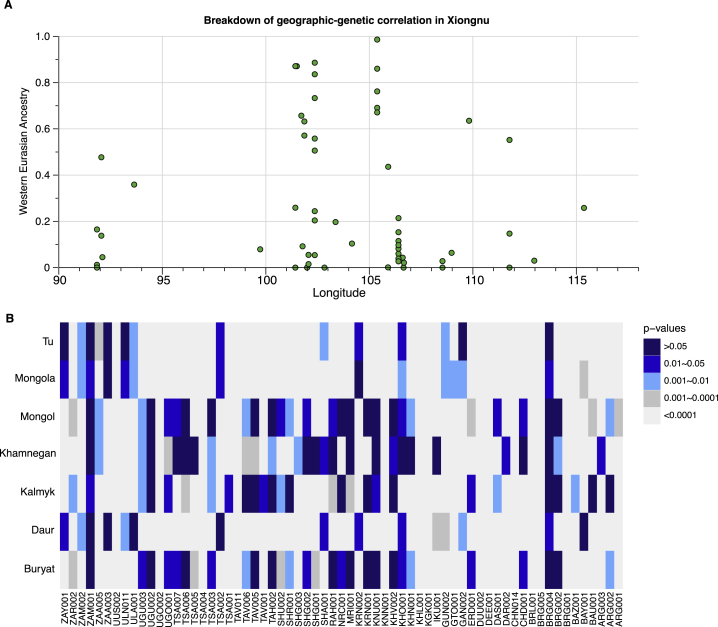
(A) Breakdown of the geographic-genetic correlation in Xiongnu. We show the proportions of West Eurasian ancestry on all individuals/groups from Xiongnu era (y axis) versus the longitude of archaeological site they come from (x axis). The raw numbers of individual estimates can be found in Table S5G for models using Sarmatian as the western Eurasian source. Unlike MLBA/EIA individuals (Figure 3), Xiongnu individuals from more western sites do not have higher proportion of western Eurasian ancestry than those from eastern sites.
(B) Comparing genetic homogeneity between ancient Mongol individuals and seven present-day Mongolic-speaking populations using qpWave. We report the p-value for every individual-based qpWave {ancient Mongol individual; Mongolic group} using seven modern Mongolic-speaking populations: Buryat, Daur, Kalmyk, Khamnegan, Mongol, Mongola, and Tu in the Human Origins dataset. When the p-value from qpWave is > 0.05, it suggests that the ancient individual on the y axis is genetically indistinguishable from the modern Mongolic-speaking population shown on the x axis. Smaller p-values indicate that the ancient individual is significantly different from the modern group.