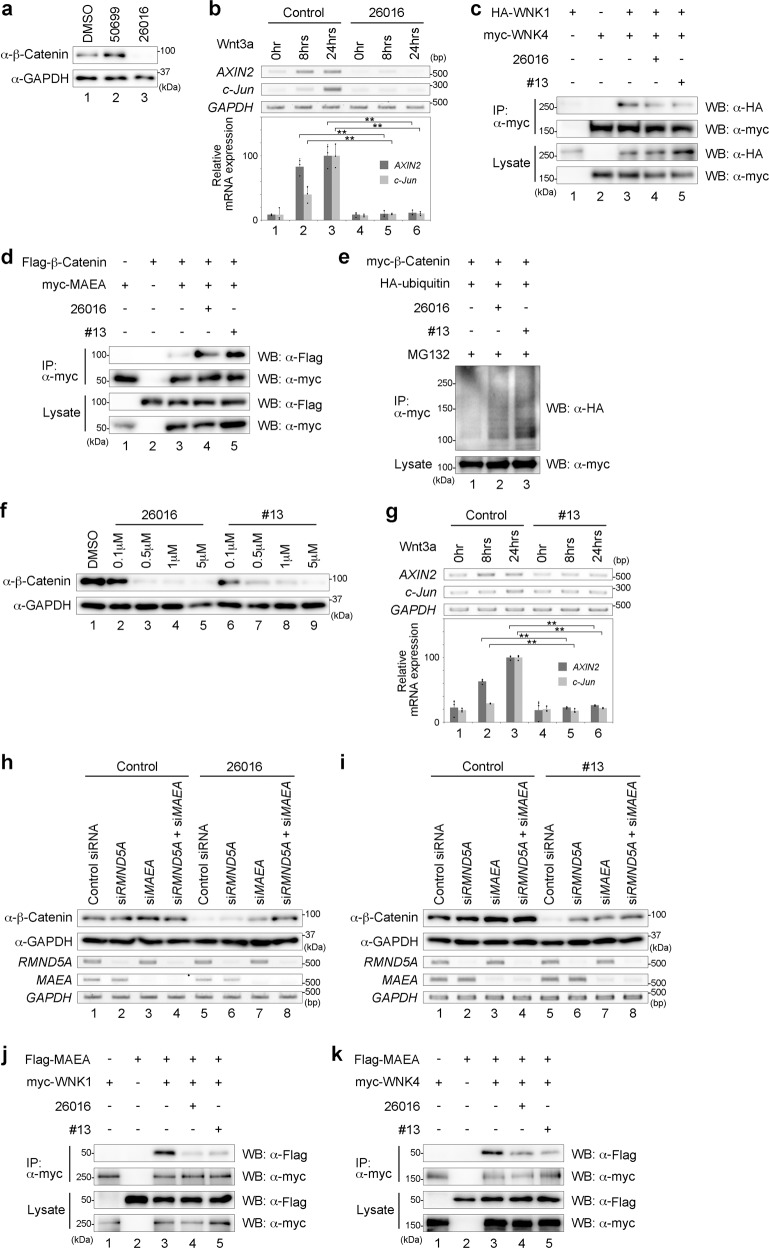
Fig. 4. WNK inhibitors function as Wnt inhibitors.
a Western blot analysis of endogenous β-Catenin following treatment with 26016 in SW480 cells. b Gene expression was examined by RT-PCR or quantitative RT-PCR in HEK293T cells following Wnt stimulation or treatment with 26016. n = 3 biologically independent experiments. Dots indicate individual data. c The interaction between WNK1 and WNK4 following treatment with 26016 or #13 was examined in HEK293T cells by co-immunoprecipitation. d The interaction between β-Catenin and MAEA following treatment with 26016 or #13 was examined in HEK293T cells by co-immunoprecipitation. e Western blot analysis of ubiquitinated β-Catenin following treatment with 26016 or #13 in HEK293T cells. f Western blot analysis of endogenous β-Catenin following treatment with 26016 or #13. g Gene expression by RT-PCR or quantitative RT-PCR analysis was examined in HEK293T cells following Wnt stimulation or treatment with #13. n = 3 biologically independent experiments. Dots indicate individual data. h, i Western blot analysis of endogenous β-Catenin following the knockdown of RMND5A and/or MAEA, or treatment with 26016 (h) or #13 (i) in SW480 cells. j The interaction between WNK1 and MAEA following treatment with 26016 or #13 was examined in HEK293T cells by co-immunoprecipitation. k The interaction between WNK4 and MAEA following treatment with 26016 or #13 was examined in HEK293T cells by co-immunoprecipitation. Values and error bars express mean ± standard deviation (SD). ** indicates p < 0.005. p value was calculated by Bonferroni test.