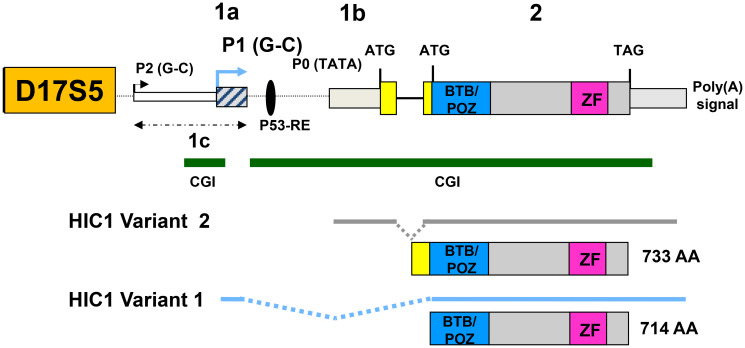
Figure 1. Genomic organization of the human HIC1 locus.
The structure of the human HIC1 locus with a large coding exon (exon 2) and alternate 5′ exons as derived from several studies is schematically drawn [6, 22, 23]. The two major promoters called P1 and P0 as well as the minor P2 promoter generating HIC1 transcripts with heterogeneous 5′ ends are shown. For clarity, only the two major transcripts generated by alternative splicing, variant 1 (1a-containing, driven by a GC-rich promoter, NM_006497) and Variant 2 (1b-containing, driven by a TATA-box promoter NM_001098202) have been shown below the human HIC1 genomic locus [23]. The variant 1 transcripts are by far the most abundant HIC1 transcripts [22, 23]. A similar organization is found in mice [21, 22]. Two conserved CpG islands (CGI), shores and shelves identified in the human and mouse HIC1 locus are shown as green lines [10, 35].