Table 1.
Iron overload categories adapted from the HealthIron study
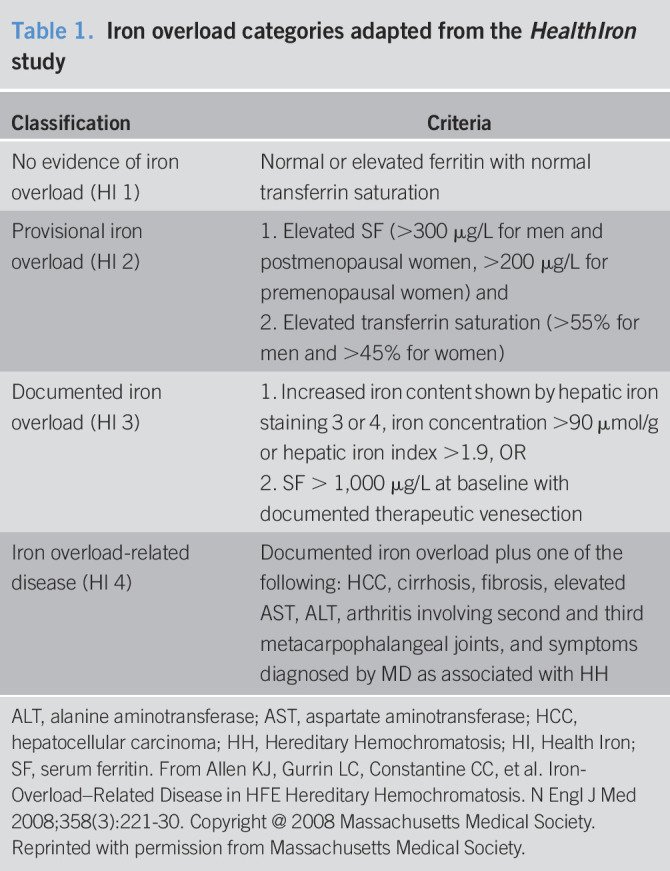
| Classification | Criteria |
| No evidence of iron overload (HI 1) | Normal or elevated ferritin with normal transferrin saturation |
| Provisional iron overload (HI 2) | 1. Elevated SF (>300 μg/L for men and postmenopausal women, >200 μg/L for premenopausal women) and 2. Elevated transferrin saturation (>55% for men and >45% for women) |
| Documented iron overload (HI 3) | 1. Increased iron content shown by hepatic iron staining 3 or 4, iron concentration >90 μmol/g or hepatic iron index >1.9, OR 2. SF > 1,000 μg/L at baseline with documented therapeutic venesection |
| Iron overload-related disease (HI 4) | Documented iron overload plus one of the following: HCC, cirrhosis, fibrosis, elevated AST, ALT, arthritis involving second and third metacarpophalangeal joints, and symptoms diagnosed by MD as associated with HH |
ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; HH, Hereditary Hemochromatosis; HI, Health Iron; SF, serum ferritin. From Allen KJ, Gurrin LC, Constantine CC, et al. Iron-Overload–Related Disease in HFE Hereditary Hemochromatosis. N Engl J Med 2008;358(3):221-30. Copyright @ 2008 Massachusetts Medical Society. Reprinted with permission from Massachusetts Medical Society.
