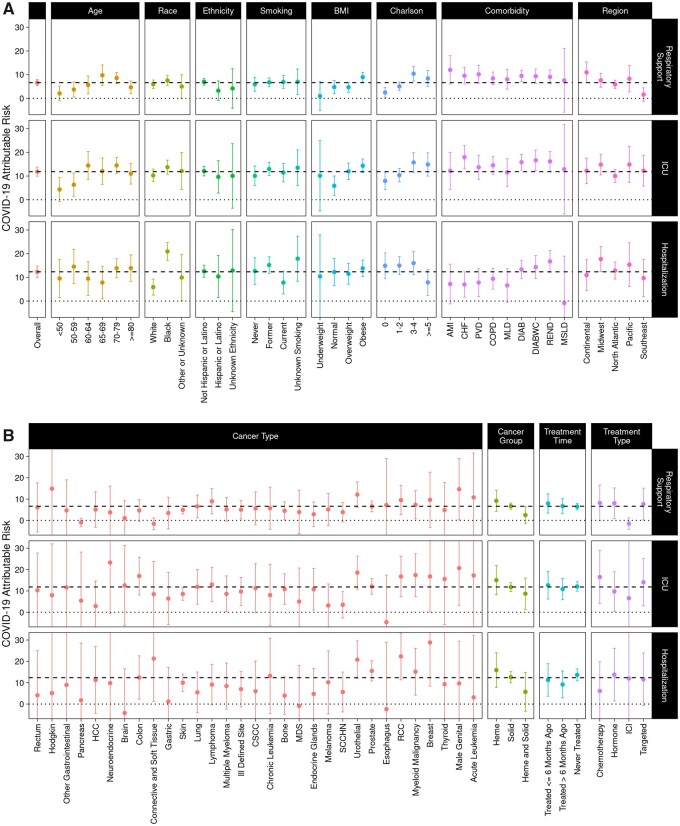
Figure 4.
COVID-19–attributable hospitalizations, ICU admissions, and respiratory support among cancer patients. COVID-19–attributable hospitalizations, ICU admissions, and respiratory support, defined as the difference in the percent of COVID-19–positive patients experiencing each outcome minus the percent of COVID-19–negative patients experiencing each outcome, are shown. Panel A shows overall data and data stratified by age, race, ethnicity, smoking, BMI, Charlson score, comorbidity, and region. Panel B shows data stratified by cancer type, cancer group, treatment time, and treatment type. 95% confidence intervals are shown. The dashed line shows the COVID-19–attributable contribution in the overall cohort, and the dotted line marks 0, the point where there is no COVID-19–attributable contribution. AMI = acute myocardial infarction; BMI = body mass index; CHF = congestive heart failure; COPD = chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; CSCC = cutaneous squamous-cell carcinoma; DIAB = diabetes without complications; DIABWC = diabetes with complications; HCC = hepatocellular carcinoma; Heme = hematological malignancy; ICI = immune checkpoint inhibitor; ICU = intensive care unit; MDS = myelodysplastic syndromes; MLD = mild liver disease; MSLD = moderate or severe liver disease; PVD = peripheral vascular disease; RCC = renal cell carcinoma; REND = renal disease; SCCHN = squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck; Solid = solid tumor.