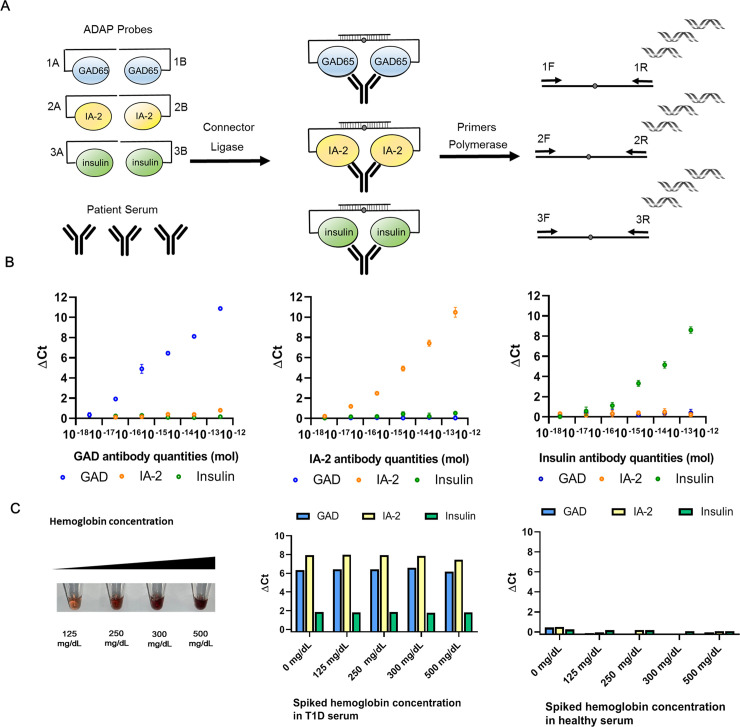
Fig 1. Schematic of sample-sparing ADAP assay for detection of multiple islet autoantibodies and the analytical characterization.
(A) The workflow of ADAP is consisted of three steps. First, 1μL of serum is incubated with islet antigen conjugate probes harboring distinct DNA barcode pairs for 30 min. The multivalency of target autoantibodies agglutinates the cognate antigen-DNA conjugate pairs into close proximity. Secondly, the addition of a ligase and a bridge oligonucleotide reunites the two-separated barcode pairs into a full length amplicon. Finally, the ligated product is PCR amplified and then quantified with distinct primer pairs in the RT-PCR. Since each antigen-DNA conjugate only has one primer binding site and thus not PCR amplifiable on its own, no washing or centrifugation step is needed to remove unreacted probes. (B) The multiplex ADAP assay detected cognate antibodies without cross-reactivity. From left to right, antibodies from immunized animals against GAD, IA-2 and insulin were serially diluted and assayed by ADAP. The x-axis displays the quantities of the antibodies in the sample. The y-axis is ΔCt calculated by the difference of Ct value between the sample and a blank (S7 Fig). Signals for GAD, IA-2 and insulin antibodies are color coded in blue, orange and green respectively. Error bars represent standard deviation from triplicate, but for many data points are too small to be visualized. (C) Tolerance of ADAP for common blood contaminant was investigated by spiking hemoglobin at various concentration in T1D and healthy serum. No interference is observed up to 500 mg/dL of hemoglobin.