Fig. 1.
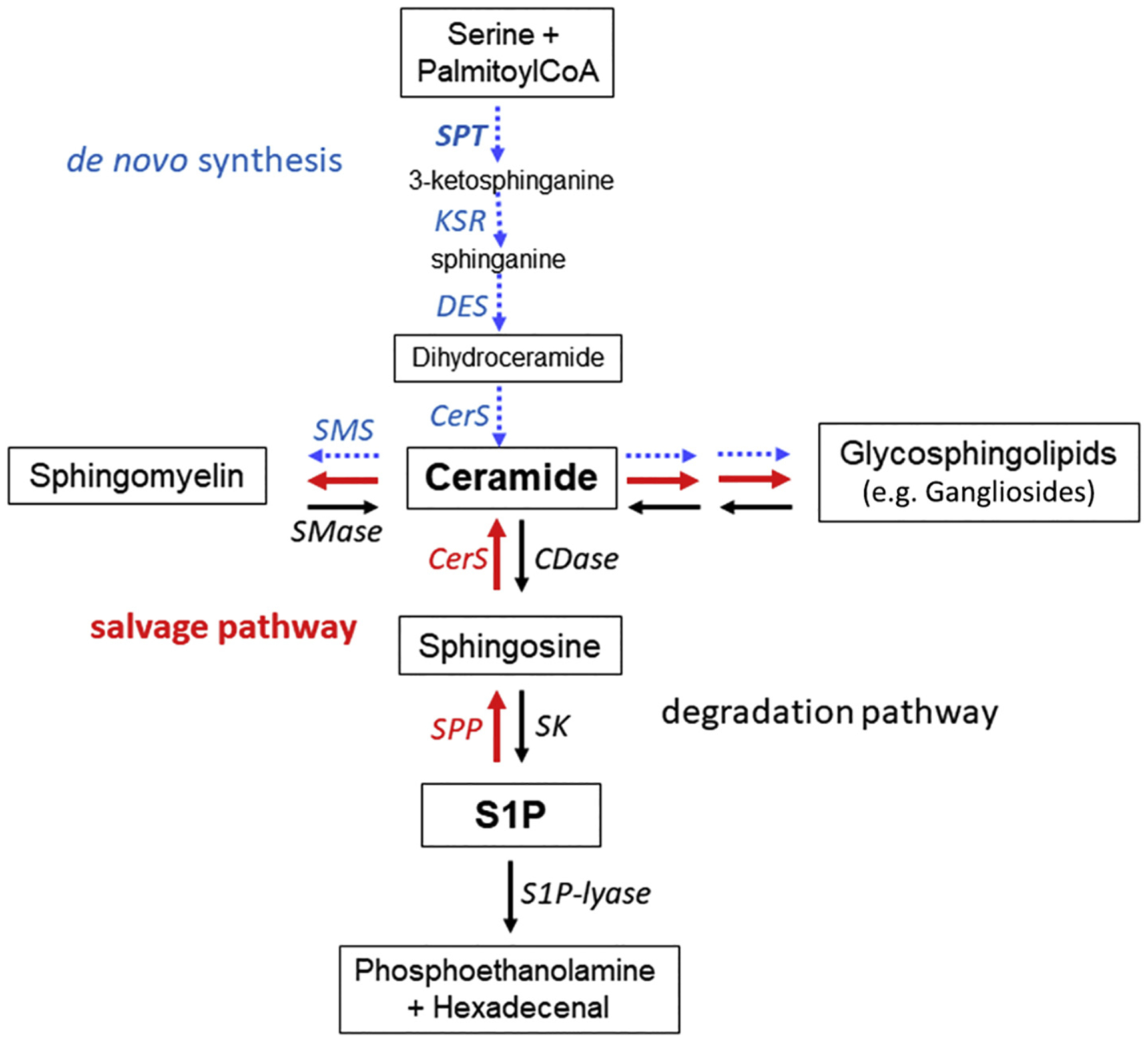
Basic scheme of sphingolipid metabolism. De novo generation of ceramide starts from serine and palmitoylCoA (blue arrows) or through recycling of sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) (red arrows). Ceramide is the degradation product, as well as the biosynthetic precursor, of all glycosphingolipids and sphingomyelin. Hydrolytic degradation of ceramide (black arrows) generates a fatty acid (not shown) and sphingosine which can, in turn, be phosphorylated to generate S1P. S1P-lyase irreversibly cleaves S1P into phosphoethanolamine and hexadecenal. Abbreviations used are: CerS, ceramide synthases (CerS1 is widespread in the brain); CDase, ceramidase (acid ceramidase is a major glycoprotein in the brain); DES, dihydroceramide desaturase; KSR, ketosphinganine reductase; SK, sphingosine kinases (SK1 and SK2 isoforms are known); SPP, S1P phosphatases (SPP1 and SPP2 isoforms are known); SMase, sphingomyelinases (acid and neutral forms are known); SMS, sphingomyelin synthase; See text for further explanations.
