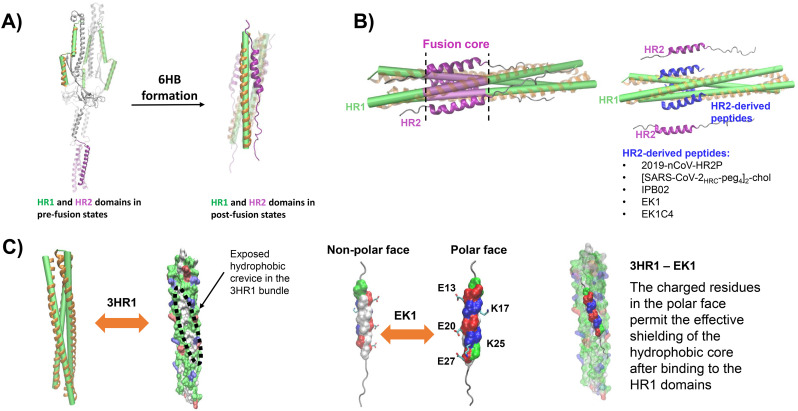
Fig. 6.
Structure and inhibition of the SARS-CoV-2 S protein fusion core. A) The HR domains of the trimeric S protein in a pre-fusion arrangement (left panel), and in the post-fusion conformation (right panel) building a six-helix bundle (6HB, PDB ID 6LXT [47]). The three heptad repeat (HR1) domains are shown as green cylinders, surrounded by orange helices, HR2 domains are depicted in purple. The long linker loop between HR1 and HR2 is depicted in grey when in the pre-fusion state. B) The HR1 domains form a three-helices bundle that serves as scaffold for the fusion core (left panel). The fusion core, shown in purple, is formed by binding of the three HR2 domains to the HR1 bundle. By binding of HR2-derived peptides (in blue) to the HR1 domains (right panel), the formation of the 6HB is inhibited. The mechanism of activity of these peptides involves their tight binding to HR1, thus preventing the association of the HR2 domains. HR1-derived peptides include IPB02 [145], EK1 [141], EK1C4 [47], 2019-nCoV-HRP2 [46] and [SARS-CoV-2HRC-peg4]2-chol [146]. C) The three HR1 domains in A) are also shown as surface projections (left panel) coloured by residue type (green: polar, red: acidic, blue: basic, white: non-polar). The molecular surface evidences open hydrophobic crevices in the regions between the helices. The EK1 peptide is presented with the molecular surface of the main interaction fragment coloured by residue type, the remaining residues are shown as a grey coil (middle panel). The surface of the interaction motif of EK1 depicts two well-defined faces with inversed polarity. Such distribution of residues allows the non-polar face to effectively couple to a non-polar crevice of the 3HR1 while the polar face shields the hydrophobic core, thus favouring the binding of this peptide (right panel). The side chains of charged residues at the polar face of EK1 are presented with sticks and the residues are labelled. The figure of the 3HR1-EK1 complex was generated using the coordinates reported with PDB ID 5ZVM [141].