Figure 1.
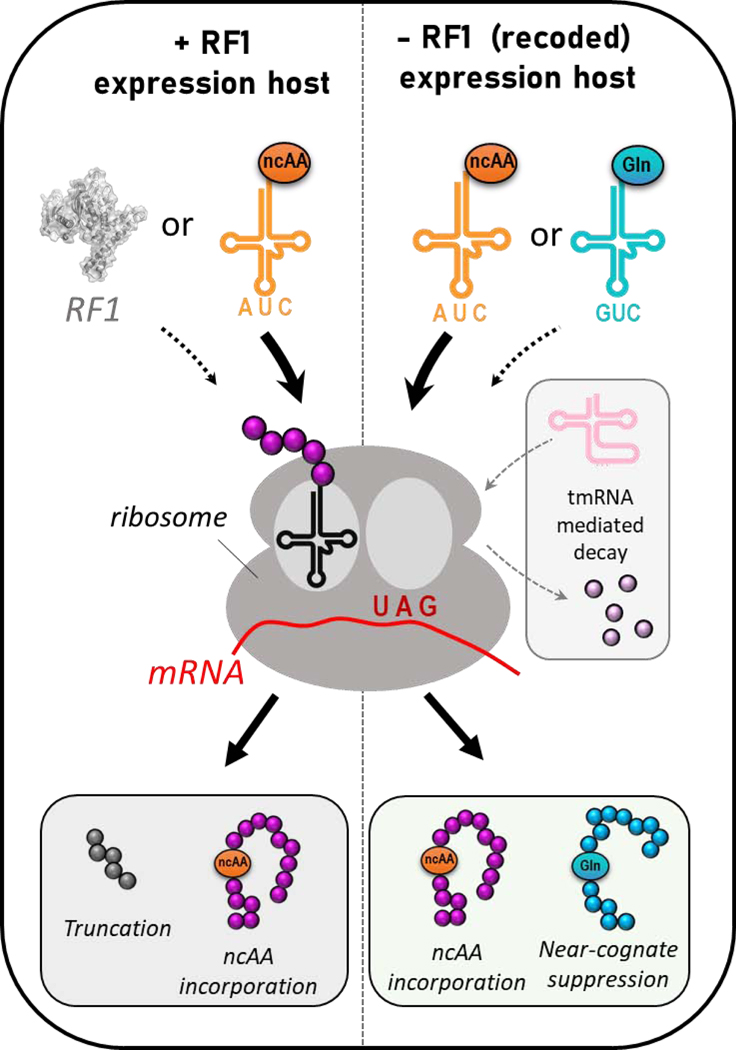
Translational outcomes for non-canonical amino acid (ncAA) incorporation into proteins at UAG amber stop codons in RF1-containing expression hosts (left) and RF1-deficient expression hosts (right). In +RF1 hosts, either ncAA-protein or truncated peptide is typically produced. In −RF1 hosts, UAG codons can be suppressed by either the GCE-derived amber suppressor tRNACUA for accurate ncAA insertion or endogenous near-cognate suppressing tRNAs which can insert e.g. Gln at UAG codons. Transfer-messenger RNA (tmRNA) can also resolve stalled ribosomes and initiate peptide decay.
