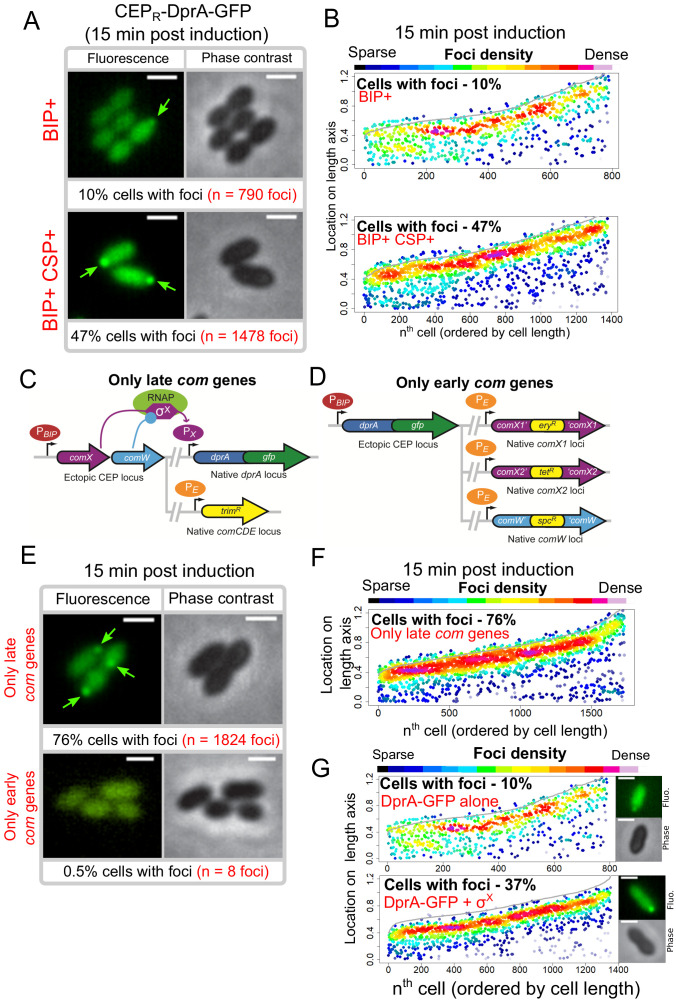
Figure 4. Polar accumulation of DprA-GFP appears to depend on late com regulon expression.
(A) Sample fluorescence microscopy images of strain R4060 producing DprA-GFP 15 min after induction with BIP or BIP and CSP. Scale bars, 1 µm. (B) Competence induction is required for optimal accumulation of DprA-GFP at the cell poles. Focus density maps as in Figure 1E. BIP+, 7845 cells and 790 foci analyzed; BIP+ CSP+, 2707 cells and 1478 foci analyzed. (C) Genetic context strain R4107 expressing dprA-gfp and only the late com regulon. PBIP and PX as in panel A, PE represents early com promoter controlled by ComE. Light blue circle, ComW; light green oval, RNA polymerase; purple hexagon, σX. (D) Genetic context of strain R4140 expressing CEPR-dprA-gfp and only the early com regulon. PBIP as in panel A, PE as in panel D. (E) Sample fluorescence microscopy images of strains producing DprA-GFP with only late (R4107) or only early (R4140) com operons 15 min after competence induction. Scale bars, 2 µm. (F) Induction of the late com regulon is required for accumulation of DprA-GFP at the cell poles. Focus density maps as in Figure 1E. 1988 cells and 1824 foci analyzed. (G) Focus density maps produced as in Figure 1E from images where DprA-GFP was produced outside of competence in presence or absence of σX. DprA-GFP alone, 7845 cells and 790 foci analyzed; DprA-GPF + σX, 3545 cells and 1355 foci analyzed. Strains used: DprA-GFP alone, R4060; DprA-GFP and σX, R4489.
Figure 4—figure supplement 1. Validation of strains expressing CEPR-dprA-gfp and the late com regulon alone.