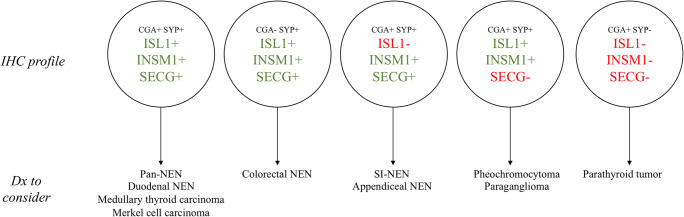
Fig. 3.
Schematic overview of the general second-generation neuroendocrine marker profiles and a suggested way of thinking regarding potential staining outcomes in metastatic NENs with an unknown primary. Most notably, NENs with immunoreactivity towards all three neuroendocrine markers of the second generation could constitute tumors with a wide variety of origin, whereas the triad ISL−, INSM1+, and SECG+ could indicate an origin in the small intestine or appendix. Additional tumor-specific markers not included in this study (serotonin, CDX2) could help verify this. A tumor exhibiting ISL1+, INSM1+, and SECG− should raise the suspicion of a pheochromocytoma or paraganglioma, and supplementary markers (GATA3, S100) are recommended. Please note that this scheme does not account for MiNEN and non-NENs with focal neuroendocrine differentiation, as these diagnoses are dependent on the proportion of tumor cells with neuroendocrine differentiation and hence could be differential diagnoses for tumors with all the abovementioned staining patterns. IHC, immunohistochemistry; +, positive or focal positive immunoreactivity; −, negative immunoreactivity; dx; differential diagnoses