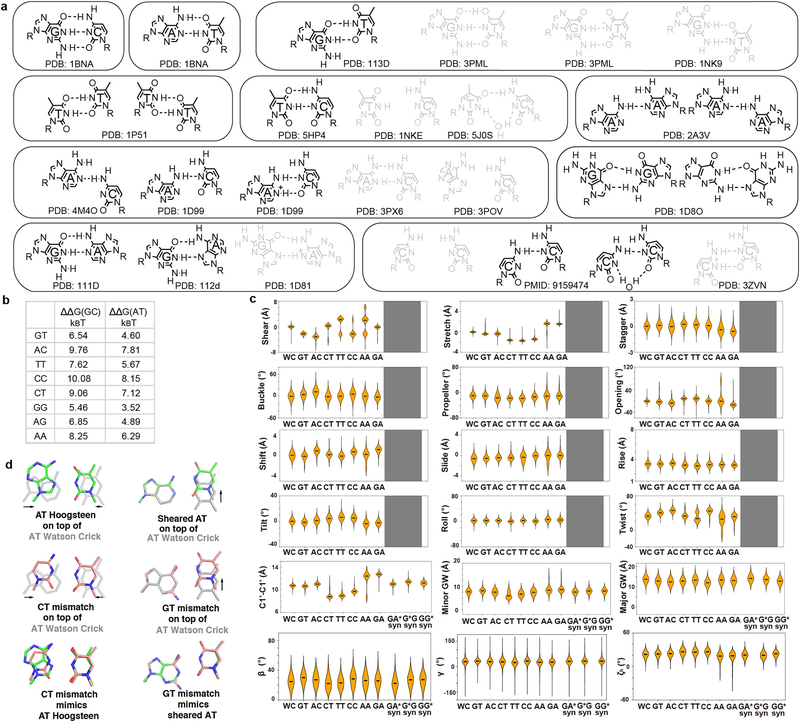
Extended Data Figure 2.
(a) Base pairing geometry of Watson-Crick base pairs and mismatches, obtained from a survey of crystal structures in the PDB34. Mismatches with modified bases and those that were metal-mediated were excluded from analysis (Methods). Predominant base pairing geometries under neutral pH conditions are shown in black. Minor geometries are shown in grey.
(b) Melting energies for DNA mismatches relative to G-C and A-T Watson-Crick base pairs. See Methods for details.
(c) Distributions of structural parameters in Watson-Crick and mismatched DNA, from MD simulations. Solid lines denote the median value of each parameter. Observations from the MD simulation results: (1) G-T retains wobble geometry during the MD simulation, with sheared conformation (|shear| around 2 Å) accompanied by a slight stretch. (2) T-T shows wobble geometry with sheared conformation (|shear| around 2 Å). Different from G-T, the T-T mismatch shows rapid dynamic equilibrium of both wobble geometries with either one of the Ts shifted to the minor groove direction. Despite this rapid dynamic equilibrium, the T-T base pair is still constricted with C1′-C1′ distance 8–9.5 Å. (3) Similar to T-T, the C-T mismatch is also constricted with two H-bonds stably formed for most of the time. However, C-T mismatch can transiently adopt a high-energy conformation with only one H-bond and is not constricted anymore (C1′-C1′ distance ~10 Å), potentially due to the close contact between T-O2 and C-O2. The entire C-T MD trajectory is comprised of approximately 5% of these high-energy species. (4) C-C is partially constricted with C1′-C1′ distance around 9.8 Å due to unstable H-bonding. (5) All pyrimidine-pyrimidine mismatches are stacked in the helix without swing out of the helix in the MD trajectories. (6) G-G does not experience anti-syn equilibrium during the simulation. The C1′-C1′ distance of G-G (G(syn)-G(anti) or G(anti)-G(syn)) is around 11.2–11.5 Å, which is larger than the canonical G-C base pair. (7) G(anti)-A(syn) is not constricted (C1′-C1′ distance around 11Å) and G(anti)-A(anti) reveals large C1′-C1′ distance around 12.8 Å. Base pair and base step parameters of bases with syn conformation (marked with *) were not computed, and are thus greyed out, due to an ill-defined coordinate frame (Methods). The C1’-C1’ distance is shown, since it is not affected by the change of coordinate frame.
(d) Mismatches can mimic distorted base-pair geometries observed in protein-bound DNA. Figure shows overlays of distorted (colored) and idealized WC (grey) base pairs from 3DNA (top); mismatches (colored) and idealized WC (gray) base pairs (middle); and mismatched and distorted WC base pairs (right). The mismatched conformations are of free DNA and were obtained from MD simulations (Methods). The C-T mismatch can mimic an A-T Hoogsteen base pair by constricting the C1′-C1′ distance (taken from PDB: 3KZ8). The G-T mismatch can mimic a sheared A-T base pair by shifting the T to the major groove direction (taken from PDB: 4MZR).