Figure 2. Intersectional ablation of peripheral and adrenal NPYDBH cells.
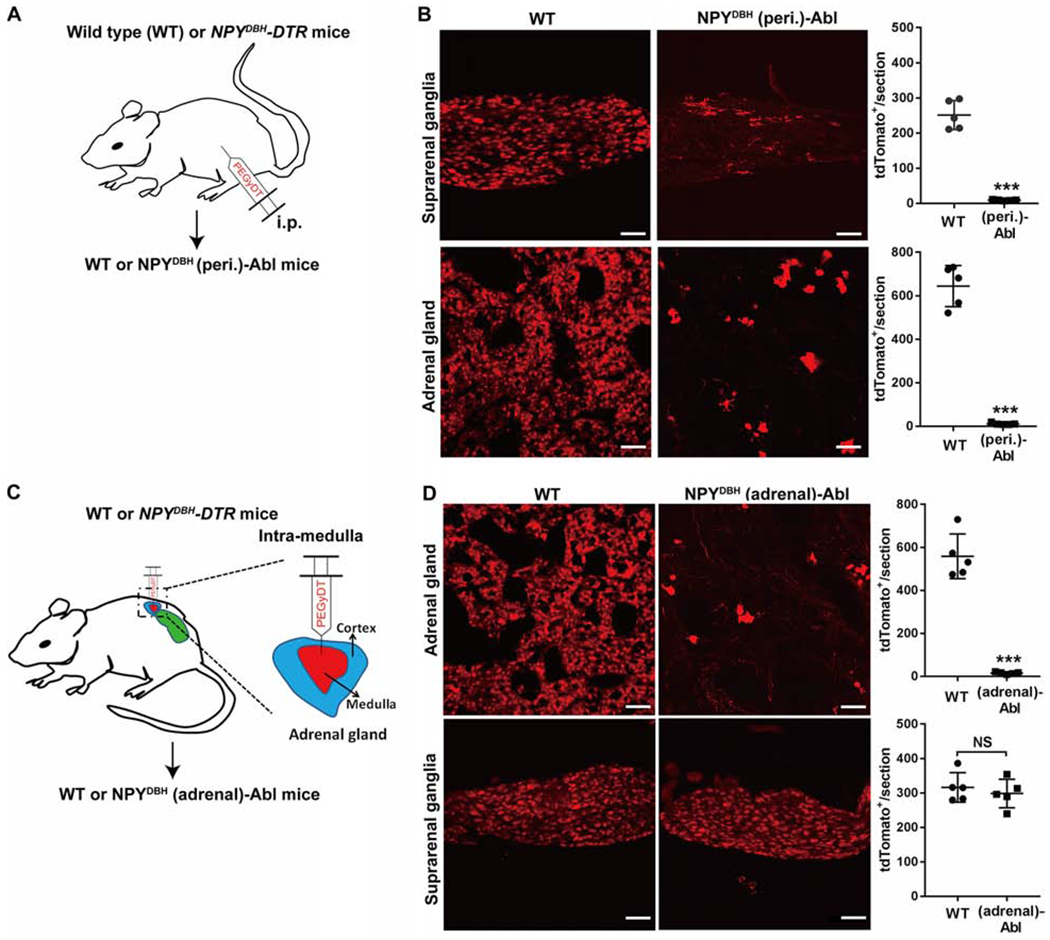
(A) Intraperitoneal injection (i.p.) of PEGyDT to create NPYDBH (peri.)-Abl [“(peri.)-Abl”] mice. “WT”: wild type littermates. All NPYCre cells were labeled by tdTomato from an unshown reporter allele. (B) Ablation of NPYCre-tdTomato+ cells in suprarenal ganglia (t8 = 13.1, ***P < 0.001) and adrenal glands (t8 = 14.96, ***P < 0.001).
(C) Intra-adrenal medulla injection of PEGyDT to create NPYDBH (adrenal)-Abl mice [“(adrenal)-Abl”].
(D) Ablation of NPYCre-tdTomato+ cells in adrenal glands, but not in suprarenal ganglia compared with WT mice (adrenal, t8 = 11.68, ***P < 0.001; suprarenal, t8 = 0.659, NS, no significant, P = 0.528).
n = 5 mice for all groups. Two-side student’s unpaired t-test in B and D. Data are shown as mean ± SEM. Scale bars, 100 μm.
