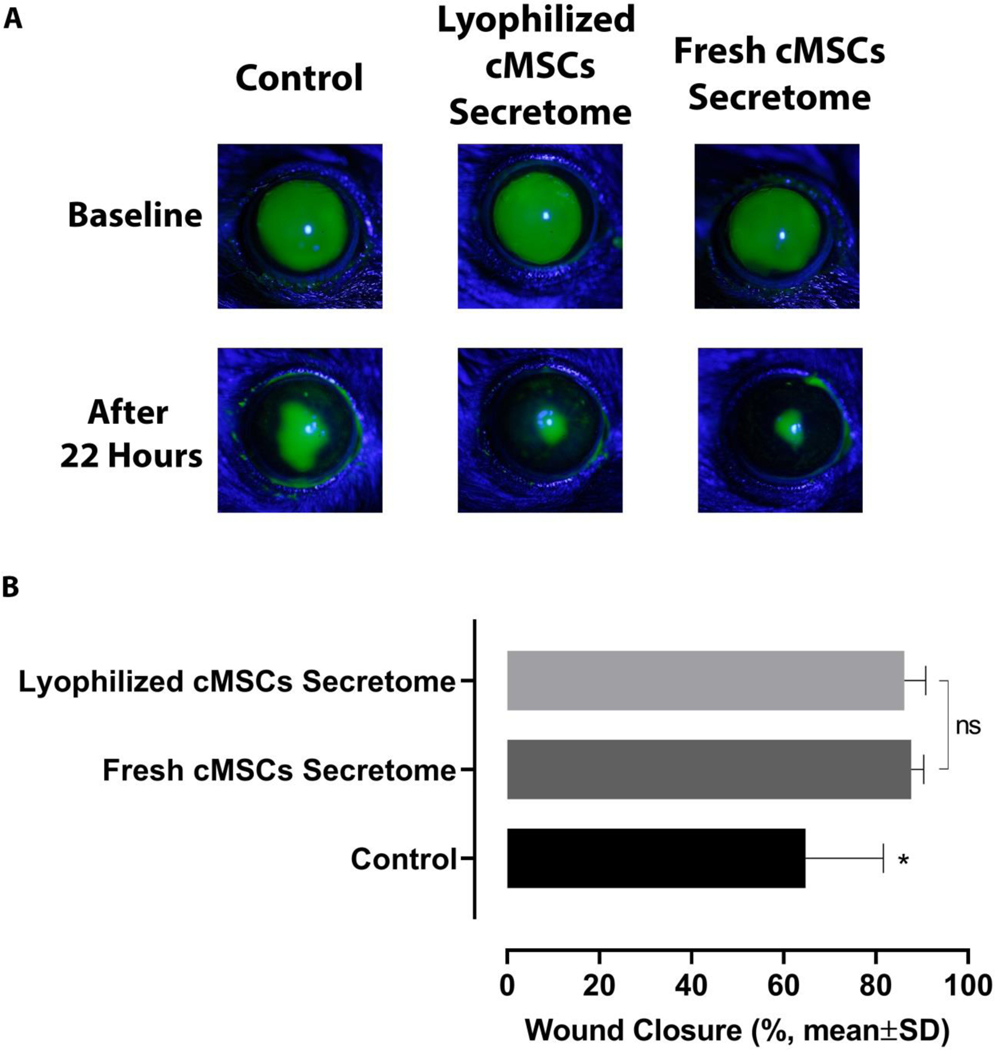
Figure 3:
The effects of lyophilized or fresh cMSCs-derived conditioned-medium on corneal epithelial wound healing following corneal epithelial debridement (2.5 mm) in mouse model compared with control. Representative images (A) show greater closure of wound in eyes treated with fresh or freeze-dried cMSCs-derived conditioned-media compared with control after 22 hours. Quantitative measurement of healed epithelial wounds (B) shows that topically applied fresh or lyophilized cMSCs conditioned-medium resulted in 87.6±2.7% and 86.1±4.6% closure, respectively; while, the mean wound closure percentage was 64.7±16.8% in control eyes. There was no significant difference between fresh and lyophilized cMSCs’ conditioned-medium (*, P<0.05, ns, Not Significant, N=10 eyes per group).