FIGURE 1.
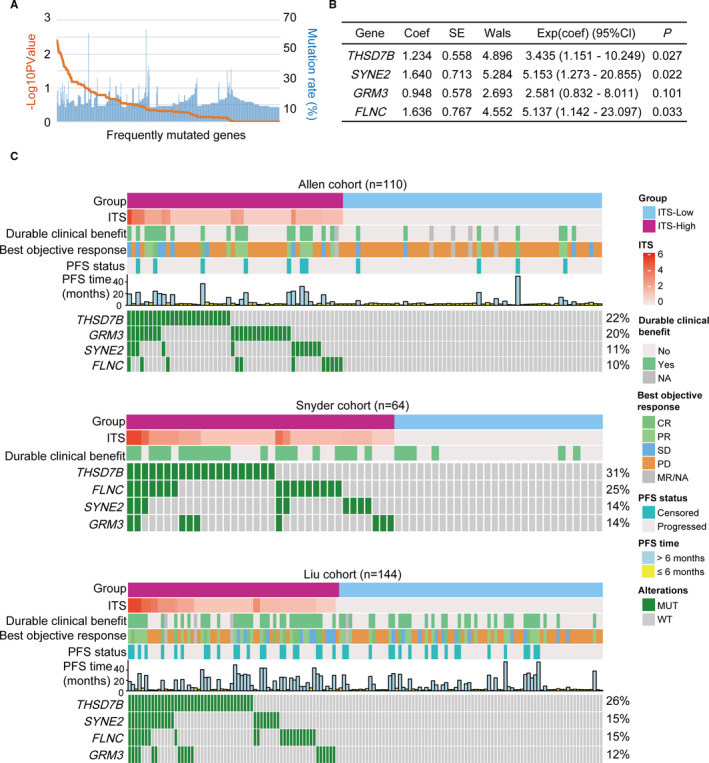
Construction of the genetic mutation model for predicting durable clinical benefit from ICIs therapy in melanoma using multivariate logistic regression analysis. (A) The frequently mutated genes (mutation rate ≥10%) ranked by p value. p value was calculated to evaluate the association between the frequently mutated genes and durable clinical benefit by a two‐sided χ 2 test. (B) Genetic mutation model was constructed by multivariate logistic regression analysis for predicting DCB from ICIs therapy. (C) Waterfall plot showing the characteristics associated with the genetic mutation model in the Allen cohort, Snyder cohort, and Liu cohort. The immunotherapy score formula was as follows: ITS = 1.234 × THSD7B + 1.640 × SYNE2 + 0.948 × GRM3 + 1.636 × FLNC. The mutation status was regarded as 1, whereas wild type is 0. ICIs, immune checkpoint inhibitors; ITS, immunotherapy score; DCB, durable clinical benefit; PFS, progression‐free survival; CR, complete response; PR, partial response; SD, stable disease; PD, progressive disease; MR, mixed response; NA, not available; Coef, coefficient; CI, confidence interval; SE, standard error
