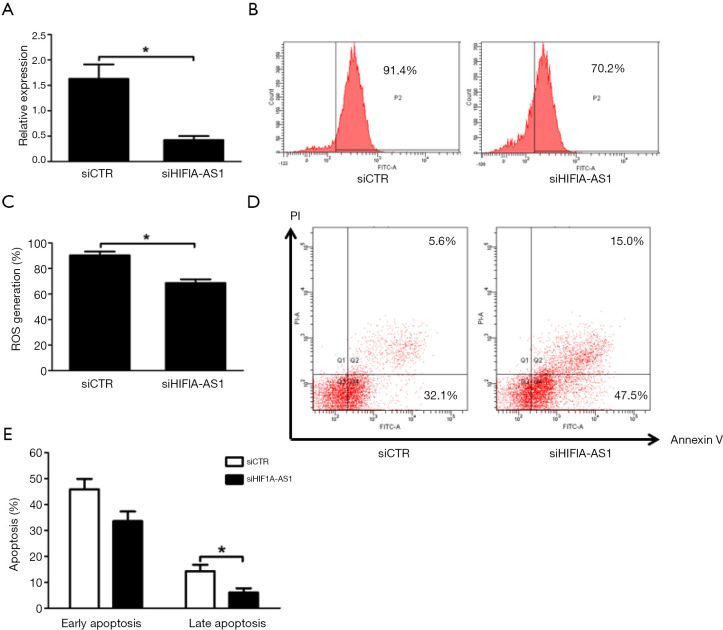
Figure 2.
Knockdown of HIF1A-AS1 attenuates oxidative stress and apoptosis of cardiomyocytes treated with CVB3. (A) The efficiency of HIF1A-AS1 knockdown by siRNA was determined by quantitative RT-PCR. (B) Flow cytometry was performed to illustrate the role of HIF1A-AS1 depletion on reactive oxygen species (ROS) production in response to CVB3 infection, which reflected the severity of intracellular oxidative stress. (C) Statistical results for the percentage of ROS production were obtained by flow cytometry analysis. (D,E) The early and late apoptosis ratio of primary cardiomyocytes transfected with control siRNA and HIF1A-AS1 siRNA was analyzed by Annexin V-PI assay and flow cytometry. Mouse cardiomyocytes were transfected with control siRNA and HIF1A-AS1 siRNA for 48 hours and then stimulated by CVB3 for 3 days. Data are mean ± SEM and representative of three separate experiments. *, P<0.05. ROS, reactive oxygen species; siCTR, control siRNA.