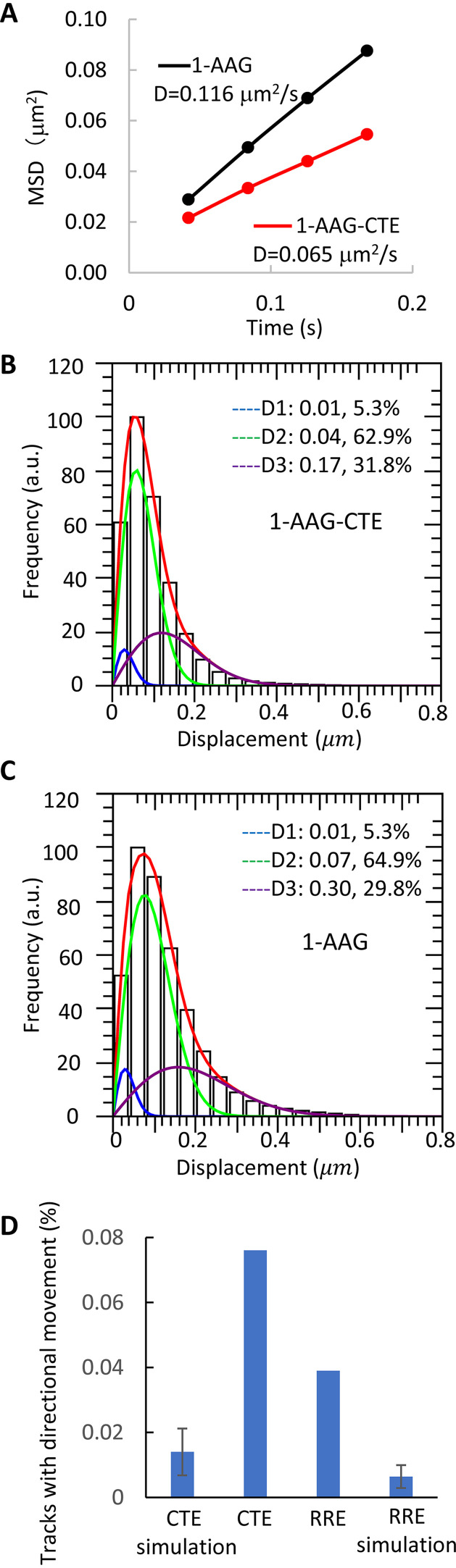
FIG 2.
Mobility and directionality of cytoplasmic HIV-1 RNAs exported via different pathways. (A) Mean square displacement (MSD) analyses of 1-AAG-CTE (red) and 1-AAG (black) RNA. D, diffusion coefficient. (B and C) Distributions of the one-step jump distance of 1-AAG-CTE RNA (B) and 1-AAG RNA (C). Data were binned (40-nm bin size) and normalized to the bin that contained the most events, which was set to 100. x axis, one-step jump distance (displacement); y axis, frequency in arbitrary units (a.u.). The distributions were fitted with a three-component model using a constant diffusion coefficient (D1 = 0.01 μm2/s) to represent the stagnant fraction or mobility under the detection limit in our system. The solid red line represents the fitted curve, and the three dotted lines indicate distributions for each of the mobility fractions. The percentages shown are proportions of each fraction. (D) Proportion of RNA tracks with directional movement, which is defined as a segment that moved with a persistence index of ≥0.7 for ≥25 consecutive steps. Simulation was performed to generate 100 sets of random-walk tracks, with each set containing the same number of tracks, distribution of track length, and the same proportions of three diffusion coefficients based on results from 1-AAG-CTE or 1-AAG RNAs.