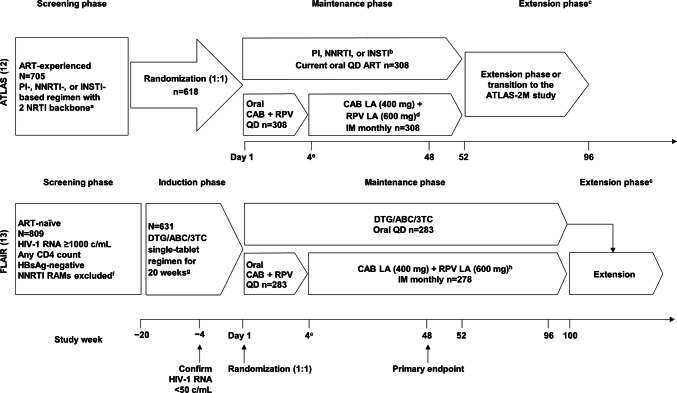
Fig. 1.
The ATLAS [12] and FLAIR [13] study design. Eligible individuals were randomly assigned (1:1) to continue their current antiretroviral regimen (CAR arm) or switch to the long-acting regimen (LA arm). Those assigned to the LA arm initially received 4 weeks of oral CAB+RPV QD, then transitioned to the injectable regimen. aUninterrupted ART for 6 months and VL < 50 c/mL at screening, 2 × VL < 50 c/mL for ≤ 12 months. bINSTI-based regimen capped at 40% of enrollment; Triumeq excluded from study. cOptional switch to CAB+RPV LA at week 52 for those on CAR. dParticipants who withdraw/complete CAB+RPV LA must complete 52 weeks of follow-up. eParticipants received an initial loading dose of CAB LA (600 mg) and RPV LA (900 mg) at week 4b. From week 8 onwards, participants received CAB LA (400 mg)+RPV LA (600 mg) injections every 4 weeks. fNNRTI RAMs but not K103N were exclusionary. gOf the 631 participants who entered the induction phase, two withdrew prior to receiving study drug. DTG plus two alternative non-ABC NRTIs was permitted if participant was intolerant or HLA-B*5701-positive (n = 30 as last regimen during induction: n = 2 discontinued during induction, n = 14 randomized to CAB+RPV LA, n = 14 randomized to DTG/ABC/3TC arm and continued on DTG plus two alternative non-ABC NRTIs in the maintenance phase). hParticipants who withdraw/complete CAB+RPV LA enter 52-week long-term follow-up. 3TC lamivudine, ABC abacavir, ART antiretroviral therapy, CAB cabotegravir, CAR current antiretroviral regimen, DTG dolutegravir, IM intramuscular, INSTI integrase strand transfer inhibitor, HBsAg hepatitis B surface antigen, LA long-acting, NNRTI non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor, NRTI nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor, PI protease inhibitor, RAM resistance-associated mutation, RPV rilpivirine, VL viral load